Hey there! Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of introductions? We’re about to embark on a journey where we’ll explore the power and importance of these opening statements. From blog posts to speeches, introductions are the gateway to capturing your audience’s attention and setting the tone for what’s to come. Think of an introduction as the front door of a house.
It’s the first impression your readers or listeners get, and it determines whether they’ll be eager to step inside or hesitant to venture further. Just like a well-decorated foyer, a compelling introduction grabs attention, piques curiosity, and creates a sense of anticipation. Whether you’re an aspiring writer, a seasoned content creator, or someone who simply wants to enhance their communication skills, understanding the art of crafting effective introductions is crucial.
It’s like having the key to unlock doors that lead to engaging conversations, thought-provoking discussions, and memorable experiences. So, join me on this adventure as we unravel the secrets behind captivating introductions. Together, we’ll explore the different techniques, strategies, and creative ways to ensure that your opening statements leave a lasting impact.
Trust me, once you master the art of introductions, you’ll have the power to captivate any audience and make your content shine. Get ready to open doors, grab attention, and create connections. The world of introductions awaits!
Table of Contents
What is a 12 volt inverter?
When it comes to choosing between a parallel 12 volt inverter and a series 12 volt inverter, it’s important to understand the differences and decide which one suits your needs better. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages. A parallel 12 volt inverter is designed to connect multiple batteries in parallel, which means the positive terminals are connected to each other and the negative terminals are connected to each other.
This configuration allows for increased power output and longer runtime. It is a great option if you need to power multiple devices simultaneously or if you require a higher wattage output. On the other hand, a series 12 volt inverter is designed to connect multiple batteries in series, which means the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next battery.
This configuration increases the overall voltage, while the amp hour capacity remains the same. A series 12 volt inverter is beneficial if you need a higher voltage output for specific devices or if you need to power devices at a longer distance. Ultimately, the decision between a parallel and series 12 volt inverter depends on your specific power needs.
If you need more power output and longer runtime, a parallel configuration may be the better choice. If you require a higher voltage output or need to power devices at a longer distance, a series configuration may be more suitable. It’s important to carefully assess your power requirements and choose the option that best meets your needs.
Parallel 12 volt inverter
When it comes to choosing between a parallel 12-volt inverter and a series 12-volt inverter, it really depends on your specific needs and preferences. Both options have their own advantages and disadvantages. A parallel 12-volt inverter is beneficial in situations where you require a higher power output.
By connecting multiple inverters in parallel, you can increase the total power capacity. This is particularly useful if you have high-power devices or appliances that need to be powered simultaneously. Additionally, parallel inverters offer redundancy and increased reliability.
If one inverter fails, the others can continue to provide power without any interruption. On the other hand, a series 12-volt inverter is better suited for applications where power stability is crucial. In a series configuration, the voltage is increased while the power output remains the same.
This allows for a more stable power supply, which is ideal for sensitive electronics and equipment. Plus, series inverters often have higher efficiency ratings compared to parallel inverters, meaning they waste less energy during the conversion process. In the end, it’s essential to consider your power requirements, the devices you’ll be using, and your overall budget when deciding between a parallel or series 12-volt inverter.
It’s also worth noting that some inverters can be switched between parallel and series configurations, giving you the flexibility to adapt to different situations. So, take the time to evaluate your needs and choose the option that best suits you.
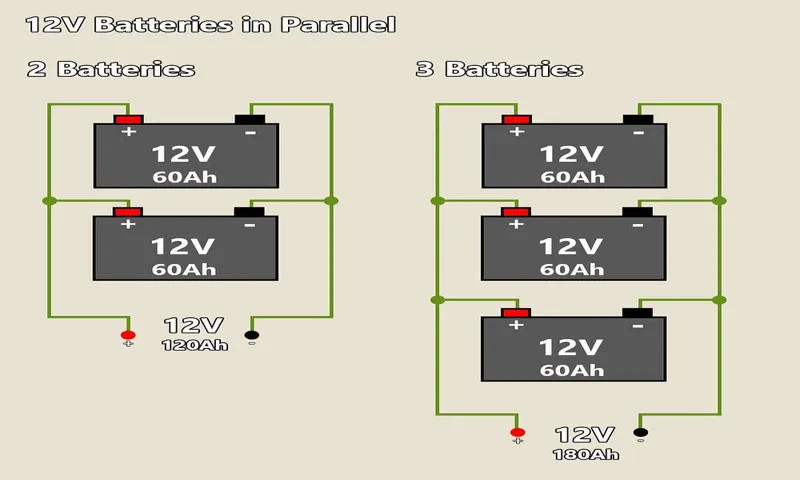
How does parallel 12 volt inverter work?
parallel 12 volt inverter, inverter, 12 volt power system, electrical power, parallel connection, power output, battery banks, flexibility, backup power. In a 12 volt power system, a parallel 12 volt inverter enhances the electrical power output by connecting two or more inverters together. This configuration provides increased power capacity and flexibility.
Instead of relying on a single inverter, a parallel connection allows for the combined power output of multiple inverters. For example, if each inverter has a power output of 2000 watts, connecting two inverters in parallel results in a total power output of 4000 watts. This can be extremely useful in situations where more power is required, such as running high-power appliances or equipment.
Furthermore, parallel inverters greatly enhance the reliability of the system. In case one inverter fails or malfunctions, the others can continue to supply power, ensuring uninterrupted electrical supply. This feature makes parallel inverters ideal for applications that require a backup power source, such as off-grid or emergency power systems.
To set up a parallel 12 volt inverter system, each inverter is connected to the same battery bank. The inverters need to have compatible voltages and be of the same type. The battery bank should also have enough capacity to handle the combined power output of the inverters.
In conclusion, a parallel 12 volt inverter is an effective way to increase the power output and reliability of a 12 volt power system. By connecting multiple inverters in parallel, it allows for greater flexibility, higher power capacity, and backup power. It is important to ensure that the inverters and the battery bank are properly matched to ensure optimal performance.
Advantages of parallel 12 volt inverter
parallel 12 volt inverter. Parallel 12 volt inverters offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for powering various devices and appliances. One of the key advantages is increased power output.
By connecting multiple 12 volt inverters in parallel, you can effectively increase the total power output. This can be especially useful when you need to power high-demand devices or appliances that require a lot of power to operate. Another advantage of parallel 12 volt inverters is improved reliability.
With multiple inverters working together, there is redundancy in case one of the inverters fails. This ensures that you have a backup power source and can continue to operate your devices or appliances even if one inverter stops working. Additionally, parallel 12 volt inverters offer increased flexibility.
You can easily add or remove inverters from the parallel setup depending on your power needs. This allows for scalability and adaptability, making it easier to adjust your power setup as required. Furthermore, parallel 12 volt inverters can also provide faster charging for batteries.
By connecting multiple inverters in parallel, you can distribute the charging load more efficiently, resulting in shorter charging times for your batteries. In conclusion, parallel 12 volt inverters offer several advantages including increased power output, improved reliability, flexibility, and faster battery charging. These advantages make them a popular choice for various applications where reliable and scalable power is required.
Series 12 volt inverter
If you’re considering investing in a 12 volt inverter, you may be wondering which is better: a parallel 12 volt inverter or a series 12 volt inverter. While both options have their own advantages, the choice ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. A parallel 12 volt inverter is designed to provide a higher power output by combining the power of multiple inverters.
This means that if one inverter fails, the others can still continue to operate. This can be beneficial in situations where reliability and continuity of power supply are critical, such as in emergency backup systems. Additionally, a parallel 12 volt inverter allows for flexibility in terms of expandability, as you can easily add more inverters to increase the power output.
On the other hand, a series 12 volt inverter is designed to provide a higher voltage output by connecting inverters in a series circuit. This can be advantageous if you require a higher voltage for your specific application, or if you need to transmit power over longer distances. However, it’s important to note that if one inverter fails in a series configuration, the entire system will fail.
This means that reliability may be a concern with a series 12 volt inverter. In summary, both parallel and series 12 volt inverters have their own unique benefits and considerations. If you prioritize reliability and expandability, a parallel 12 volt inverter may be the better choice for you.
On the other hand, if you require a higher voltage output or need to transmit power over longer distances, a series 12 volt inverter may be more suitable. Ultimately, it’s important to evaluate your specific needs and consult with a professional to determine the best option for your situation.
How does series 12 volt inverter work?
series 12 volt inverter A series 12 volt inverter is a device that converts the 12-volt DC (direct current) power from a battery or other power source into 120-volt AC (alternating current) power. This allows you to power devices and appliances that typically run on household electricity, even when you’re away from an electrical outlet. The way a series 12 volt inverter works is quite fascinating.
It uses a series of electronic components, including transistors and capacitors, to convert the DC power into AC power. When the 12-volt DC power enters the inverter, it goes through a process called inversion. This involves changing the direction of the current, so it oscillates between positive and negative at a frequency of 60 hertz (Hz).
The inverter then uses transformers to increase the voltage from 12 volts to 120 volts. This allows the AC power to be compatible with the electrical devices you want to power. The high-frequency oscillation of the current is then transformed into the standard 60 Hz frequency that is used in most households.
One of the key benefits of a series 12 volt inverter is its portability. Since it runs off a 12-volt power source, such as a car battery or a portable solar panel, you can take it with you wherever you go. This makes it ideal for camping trips, road trips, or any situation where you need to power your devices away from a traditional power source.
In conclusion, a series 12 volt inverter is a handy device that allows you to convert the 12-volt DC power from a battery into 120-volt AC power. It uses electronic components to invert the current, increase the voltage, and transform the frequency to make it compatible with household appliances. Its portability makes it a convenient option for powering devices on the go.
Advantages of series 12 volt inverter
series 12 volt inverter
Which is better?
When it comes to inverters, the debate between parallel and series 12 volt options is a common one. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, but determining which one is better depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Parallel 12 volt inverters offer the advantage of increased power output.
By connecting multiple inverters in parallel, you can combine their power capacity. This is especially useful if you need to power multiple devices or if you have a high-powered appliance that requires a lot of energy. Additionally, parallel inverters allow for redundancy and improved system reliability.
If one inverter fails, the others can continue to provide power. On the other hand, series 12 volt inverters offer a different set of benefits. Series connections allow for higher voltage output, which is important for certain applications.
For example, if you need to power a device that requires a higher voltage, such as a specific type of electronic equipment, a series inverter may be the better choice. Additionally, series inverters are often more efficient, as they can handle higher power loads with less energy loss. Ultimately, the decision between parallel and series 12 volt inverters depends on the specific requirements of your situation.
Consider factors such as power needs, the type of devices you will be using, and the level of reliability you desire. It may also be helpful to consult with a professional who can assess your needs and provide guidance on which option is best for you.
Factors to consider
When it comes to deciding between renting and buying a home, there are a few factors to consider. Firstly, financial stability plays a crucial role. If you have a steady income and can afford the initial costs of purchasing a home, such as a down payment and closing costs, buying may be a better option.
Additionally, if you plan to stay in one location for a long time, buying a home allows you to build equity and potentially make a profit in the future. On the other hand, if you value flexibility and prefer not to be tied down to one location, renting may be the way to go. Renting also allows you to avoid the responsibilities and costs associated with home maintenance and repairs.
Ultimately, the decision depends on your personal circumstances and priorities. So, which is better for you? Consider the pros and cons of both options before making your decision.
Application-specific considerations
When it comes to deciding which is better between Wi-Fi and Ethernet, it really depends on the specific application and the needs of the user. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to consider the specific requirements before making a decision. One key consideration is the speed and reliability of the connection.
Ethernet generally provides a faster and more stable connection compared to Wi-Fi. This is especially important for applications that require high bandwidth, such as online gaming or streaming HD videos. If you need a reliable and fast connection, Ethernet might be the better option for you.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi offers more flexibility and convenience. With Wi-Fi, you can connect to the internet from anywhere within the range of the router. This is especially useful for devices like smartphones and tablets that are designed to be mobile.
Wi-Fi also eliminates the need for cables, making it easier to set up and manage multiple devices. Another consideration is security. While both Wi-Fi and Ethernet can be secured with passwords and encryption, Ethernet is generally considered to be more secure.
Since Ethernet connections are physical and require a direct connection to the router, it’s more difficult for outsiders to intercept the data. However, with proper security measures in place, Wi-Fi can also be safe and secure. In conclusion, there is no definitive answer to whether Wi-Fi or Ethernet is better.
It really depends on the specific application and the needs of the user. If speed and reliability are of utmost importance, Ethernet might be the better option. However, if flexibility and convenience are more important, Wi-Fi might be the way to go.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the question of whether manual or automatic transmission is better comes down to personal preference and individual circumstances. Automatic transmissions offer convenience and ease of use, especially for city driving and stop-and-go traffic. They require minimal effort from the driver and can even improve fuel efficiency in some cases.
On the other hand, manual transmissions provide a greater sense of control and engagement with the vehicle. They can be more fun to drive, especially on open roads or when seeking a more exhilarating driving experience. Manual transmissions also tend to be more durable and less expensive to repair.
In the end, it’s important to consider factors such as driving conditions, personal preferences, and budget when deciding which transmission is better for you.
Conclusion
In the battle of parallel versus series 12 volt inverters, it’s clear that the parallel option reigns supreme. Why, you ask? Well, let me enlighten you with a dose of wit and cleverness. Imagine you’re at a race.
On one side, you have the parallel 12 volt inverter, sleek and agile like an Olympic sprinter. On the other side, you have the series 12 volt inverter, plodding along like a snail with jet lag. The parallel inverter, with its ability to divide the load evenly between multiple inverters, performs like a well-oiled machine.
It’s like having a team of synchronized swimmers gracefully gliding through the water, effortlessly supporting one another. Meanwhile, the series inverter struggles to keep up. It’s like dragging a ball and chain behind you as you attempt to run a marathon.
The load is forced through one inverter at a time, causing delay and inefficiency. But it doesn’t stop there. The parallel inverter not only outperforms its counterpart in terms of speed and efficiency, but it also offers a safety net.
If one inverter fails, the others can pick up the slack, like a comedic duo in a high-wire circus act. The series inverter, on the other hand, is a one-man show. If it fails, you’re left in the darkness, feeling as stranded as a castaway on a deserted island.
So, when it comes down to it, the choice is clear. Parallel 12 volt inverters are the winners of this electrifying battle. They offer the power, efficiency, and reliability that we all yearn for in our electrical endeavors.
FAQs
Which is better, a parallel 12-volt inverter or a series 12-volt inverter?
The suitability of a parallel or series 12-volt inverter depends on the specific application.
What are the advantages of a parallel 12-volt inverter?
Some advantages of a parallel 12-volt inverter include increased power output, improved efficiency, and greater flexibility in system design.
What are the advantages of a series 12-volt inverter?
Some advantages of a series 12-volt inverter include simplified wiring, reduced voltage drop, and the ability to handle higher voltage loads.
What are the limitations of a parallel 12-volt inverter?
Some limitations of a parallel 12-volt inverter include the need for carefully matched inverters, increased complexity in system configuration, and the potential for one inverter to affect the performance of others.
What are the limitations of a series 12-volt inverter?
Some limitations of a series 12-volt inverter include the limited power output compared to a parallel configuration, potential voltage imbalances between inverters, and the increased chances of a single point of failure affecting the entire system.
How do I determine which type of 12-volt inverter is better for my needs?
To determine which type of 12-volt inverter is better for your needs, consider factors such as power requirements, load characteristics, system complexity, and desired level of redundancy.
Can I combine parallel and series 12-volt inverters in my system?
Yes, it is possible to combine parallel and series 12-volt inverters in a single system. This can provide a balance of increased power output and system redundancy. However, careful planning and configuration is required to ensure proper operation and compatibility between the inverters.


