Have you ever been out camping, only to run out of battery on your phone or portable electronic devices? Or maybe you’ve experienced a power outage at home and wished you had a backup source of electricity. That’s where a power inverter comes in handy. A power inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) power from a battery or solar panel into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to run household appliances or charge electronic devices.
It essentially “inverts” the power source to a different form that is more suitable for everyday use. Think of it like a translator for electricity. Just as a language translator converts words and phrases from one language into another, a power inverter converts electricity from one form to another.
It allows you to tap into your battery’s stored energy and use it to power devices that require AC power, like laptops, TVs, or even refrigerators. Power inverters come in various sizes and power ratings, allowing you to choose one that matches your specific needs. Some inverters are small and portable, making them perfect for camping trips or emergency situations, while others are larger and more powerful for use in homes or businesses.
In conclusion, a power inverter is a versatile device that can provide a backup source of power when you need it most. Whether you’re out camping, experiencing a power outage, or simply want to charge your electronic devices on the go, a power inverter is a reliable companion that can keep you connected and powered up.
Table of Contents
How does a power inverter work?
If you’ve ever wondered how a power inverter works, you’re not alone. Power inverters are devices that convert DC (direct current) power into AC (alternating current) power, allowing you to use devices that require AC power from a DC power source, such as a car battery or a solar panel. So, how does it do this? Let’s break it down.
Think of a power inverter as a translator. It takes the silent language of DC power and translates it into the language of AC power. Just like how a translator takes words from one language and converts them into words in another language, a power inverter takes the steady flow of DC electricity and converts it into the oscillating flow of AC electricity.
The main component in a power inverter is a circuit called an inverter bridge. This bridge consists of a series of transistors or switches that rapidly open and close to create a waveform that resembles AC power. These transistors or switches are controlled by a circuit that determines the frequency and voltage of the output AC power.
When the power inverter is connected to a DC power source, it converts the DC power into high-frequency AC power. This AC power is then fed into a transformer, which adjusts the voltage to the desired level. Finally, the transformed AC power is sent out through the outlet or socket of the power inverter, ready to power your devices.
In summary, a power inverter works by converting DC power into AC power through the use of a circuit called an inverter bridge. This bridge consists of transistors or switches that create an AC waveform, which is then adjusted to the desired voltage level through a transformer. So, the next time you use a power inverter to charge your phone or run a small appliance, you’ll have a better understanding of how it works.
DC to AC conversion
power inverter
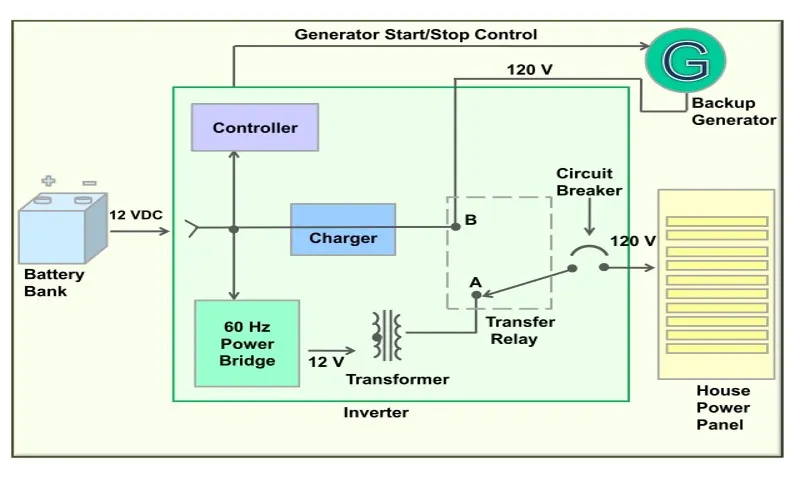
Components of a power inverter
power inverter
Types of power inverters
Have you ever wondered how power inverters work? Well, let me break it down for you. A power inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) power from a battery into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to power various appliances and devices. It acts as a bridge between your battery and the electrical appliances you want to use.
Power inverters work by using a series of complex electronic circuits to convert the DC power from the battery into AC power, which is then delivered to your devices. They essentially take the steady flow of energy from your battery and transform it into the fluctuating power required by your appliances. So next time you’re enjoying the convenience of using your electrical devices while on the go, remember that it’s all thanks to the magic of power inverters!
Modified sine wave inverters
power inverters, modified sine wave inverters, types of inverters
Pure sine wave inverters
Types of power inverters for different applications. When it comes to power inverters, there are several types available, each designed for specific applications. One type that stands out is pure sine wave inverters.
These inverters are known for their ability to produce a clean and stable sine wave output, similar to the power supplied by the utility grid. This makes them ideal for sensitive electronics and appliances, such as laptops, televisions, and medical equipment. Pure sine wave inverters are more expensive compared to modified sine wave inverters, but they offer several advantages.
For starters, they can power a wider range of devices without any issues. This is because most electronics and appliances are designed to work with pure sine wave power. Using a modified sine wave inverter might cause the device to malfunction or operate less efficiently.
In addition to the compatibility factor, pure sine wave inverters also provide a higher quality output. The clean and stable sine wave produced ensures that your devices receive a consistent source of power, which can help prolong their lifespan. It also eliminates any potential humming or buzzing noises that may be heard when using modified sine wave inverters.
Another advantage of pure sine wave inverters is their ability to reduce electrical noise. This can be useful when powering audio equipment or sensitive measurement devices that require a noise-free power source. With pure sine wave inverters, you can be confident that your equipment will perform at its best without any interference or distortion.
In conclusion, pure sine wave inverters are an excellent choice for those who require a high-quality power supply for their sensitive electronics and appliances. While they may be more expensive, they offer several benefits, including compatibility with a wide range of devices, a clean and stable power output, and reduced electrical noise. So, if you want to ensure that your devices perform optimally and last longer, it’s worth considering investing in a pure sine wave inverter.
Applications of power inverters
Have you ever wondered how power inverters work? Power inverters are incredibly useful devices that convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. This allows you to use AC-powered devices, such as laptops, televisions, and even kitchen appliances, in places where there is only DC power available, like in your car or when you’re off the grid. Essentially, a power inverter takes the energy from your car’s battery or a dedicated power source and transforms it into the type of energy that your devices need to function.
It’s like a translator, translating the language of one type of power into another. So the next time you’re camping or on a road trip and want to power your electronic devices, you’ll know that it’s all thanks to the magic of power inverters!
Inverters for use in vehicles
power inverters, vehicles, applications, inverters for vehicles
Inverters for renewable energy systems
Inverters are a crucial component of renewable energy systems, as they play a vital role in converting the DC (direct current) power produced by solar panels or wind turbines into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to power our homes and businesses. However, inverters are not only limited to residential or commercial applications. They have a wide range of applications in various sectors.
For example, inverters are used in utility-scale solar power plants to convert the DC power generated by thousands of solar panels into usable AC power that can be fed into the grid. They are also used in off-grid systems, such as remote cabins or boats, where the DC power from batteries or solar panels is converted into AC power to run appliances and lights. In addition to these applications, inverters are used in electric vehicle charging stations, where they convert the AC power from the grid into DC power that can be stored in the vehicle’s battery.
Inverters are also used in microgrids and smart grids to efficiently manage and distribute the power generated by multiple renewable energy sources. With the growing renewable energy sector, the demand for power inverters is expected to continue to rise, making them an essential component for a sustainable future.
Choosing the right power inverter for your needs
If you’re in the market for a power inverter, it’s important to understand how they work so you can choose the right one for your needs. Power inverters are devices that convert DC (direct current) power from a battery or solar panel into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to power household appliances and electronics. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil of wire is exposed to a changing magnetic field, causing an electric current to flow through the wire.
This current is then converted from DC to AC using electronic circuitry within the power inverter. The size and capacity of a power inverter will determine its power output, so it’s important to consider the specific power requirements of the devices you intend to power when choosing the right power inverter for your needs.
Wattage requirements
power inverter, wattage requirements. In order to choose the right power inverter for your needs, it’s important to understand your wattage requirements. The wattage requirements of your electronic devices will determine the size and capacity of the power inverter you need.
It’s important to consider both the continuous power and the surge power requirements of your devices. The continuous power requirement is the amount of power that the device requires to run continuously, while the surge power requirement is the amount of power that the device requires to start up or during peak usage. You can usually find the wattage requirements of your devices listed on the label or in the user manual.
Once you have a list of all your devices and their wattage requirements, you can add up the total wattage to determine the size of the power inverter you need. It’s always a good idea to choose a power inverter that has a slightly higher wattage capacity than your total requirements to accommodate any future additions or fluctuations in power usage.
Waveform compatibility
power inverter, waveform compatibility, choosing the right power inverter
Conclusion
Power inverters, the unsung heroes of modern technology, are a marvel of electrical sorcery. With their ability to convert DC power into AC power, they are like the chameleons of the electrical world, transforming the energy they receive into a different form entirely. To understand how power inverters work, imagine a sophisticated magician who can bend the laws of physics.
When you connect a power inverter to a DC power source, such as a battery or a solar panel, it behaves like a magician’s assistant, carefully teasing out the hidden potential within. Through a complex process involving semiconductors and electronic circuitry, the power inverter taps into the dormant energy and transforms it into its alter ego: AC power. Like a misunderstood superhero, power inverters secretly reign over our everyday lives.
They are the captivating force behind our ability to charge our devices on the go or power essential appliances during a blackout. Without them, our lives would be stuck in a never-ending power outage, our devices begging for a jolt of electricity. So, the next time you plug your phone into a car charger or use an emergency backup power supply, take a moment to appreciate the mystical power of the humble power inverter.
Behind that unassuming box lies a world of electrical magic, turning direct current into alternating current, and keeping us connected to the invisible webs of power that weave through our modern lives. In the grand tapestry of electrical technology, power inverters are the hidden threads that keep our world illuminated.”
FAQs
How does a power inverter work?
A power inverter converts DC (direct current) from a battery or solar panel into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to run household appliances or electronic devices.
What are the main components of a power inverter?
The main components of a power inverter include a DC input, an inverter circuit, and an AC output. Some inverters also have additional features such as built-in charging circuits or surge protectors.
How is a power inverter connected to a battery?
The power inverter is typically connected to a battery through a set of cables. The positive terminal of the battery is connected to the positive terminal of the inverter, while the negative terminals are also connected.
Can a power inverter be connected to a solar panel?
Yes, a power inverter can be connected to a solar panel to convert the DC power generated by the solar panel into AC power for use in homes or businesses.
What is the role of the inverter circuit in a power inverter?
The inverter circuit in a power inverter is responsible for converting the DC power from the input source into AC power at the desired voltage and frequency.
Can a power inverter handle heavy loads?
The capacity of a power inverter to handle heavy loads depends on its power rating. Higher power-rated inverters can handle larger loads, while lower power-rated inverters are suitable for smaller devices.
Can a power inverter be used in a vehicle?
Yes, power inverters are commonly used in vehicles to power electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, or even small appliances. They can be connected to the vehicle’s battery for power supply.



