Welcome to our blog, where we dive headfirst into the world of introductions. Whether you’re meeting someone for the first time, presenting yourself to a group, or writing an essay, introductions are an essential part of human communication. They set the stage, establish context, and create a connection between the speaker/writer and the audience.
Have you ever been in a room full of strangers, feeling a mix of excitement and apprehension? That’s exactly what the art of introduction is all about. It’s like stepping onto a stage and captaining the ship of a conversation or an event. Mastering the art of introductions can boost your confidence and create a positive and lasting impression.
But introductions don’t just happen in social settings. They also play a crucial role in written communication. When you start reading an article or a blog post, you expect a captivating introduction that grabs your attention and compels you to read further.
It’s the ultimate hook that pulls you in, much like a good opening line in a novel. Imagine a world without introductions; it would be like entering a room without any light. Introductions provide that initial spark, igniting curiosity and setting the tone for what’s to come.
They can be witty, thought-provoking, or even poignant, depending on the purpose and context. In this blog, we’ll explore different types of introductions, discuss their significance, and provide tips on how to craft the perfect introduction. We’ll delve into the psychology behind introductions, explore their impact on our daily lives, and analyze various scenarios where introductions can make or break an interaction.
So, whether you’re a budding writer, a social butterfly, or simply someone looking to make a strong first impression, stay tuned for our in-depth exploration of the power of introductions. Get ready to embark on a journey that will leave you feeling more confident and equipped to navigate any situation that requires an introduction.
Table of Contents
What is a Coolant Reservoir?
Have you ever wondered how your car’s coolant system works? One important component of this system is the coolant reservoir. Also known as the overflow tank or expansion tank, the coolant reservoir is a small plastic container located near the radiator. Its purpose is to provide a storage space for excess coolant when the engine heats up and the coolant expands.
When the engine cools down, the coolant contracts and is then drawn back into the radiator from the reservoir. This process helps to maintain a consistent coolant level in the radiator and prevents air pockets from forming. Without a functioning coolant reservoir, your engine could overheat and potentially cause serious damage.
So, the next time you check under the hood of your car, take a moment to appreciate the vital role of the coolant reservoir in keeping your engine running smoothly.
Purpose of a Coolant Reservoir
Have you ever wondered how the coolant reservoir in your car actually works? Well, let me explain it to you. The coolant reservoir, also known as the expansion tank or overflow tank, is an essential part of your vehicle’s cooling system. Its main purpose is to provide a space for coolant to expand and contract as the engine heats up and cools down.
You see, as your engine runs, it generates a lot of heat. The coolant, which circulates through the engine, absorbs this heat and helps regulate the engine’s temperature. However, as the coolant heats up, it expands, and if there was nowhere for it to go, it could cause damage to the cooling system.
That’s where the coolant reservoir comes in. It acts as a buffer, allowing the coolant to expand and contract without causing any harm. So the next time you pop open your hood and see that plastic tank filled with liquid, know that it’s there to keep your engine running smoothly and prevent overheating.
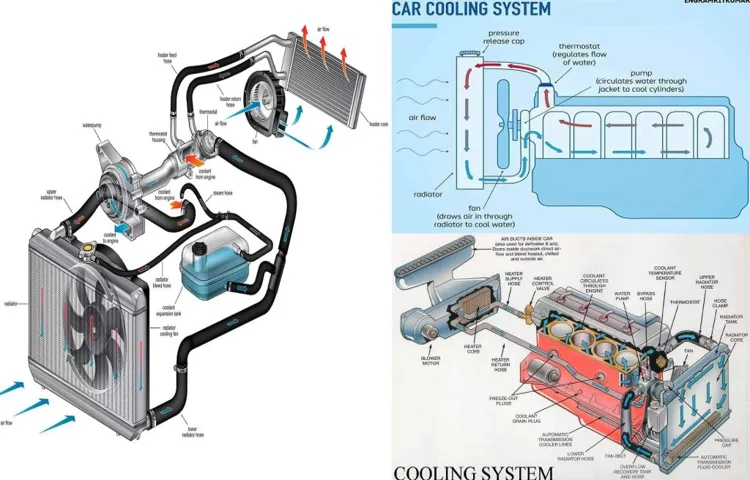
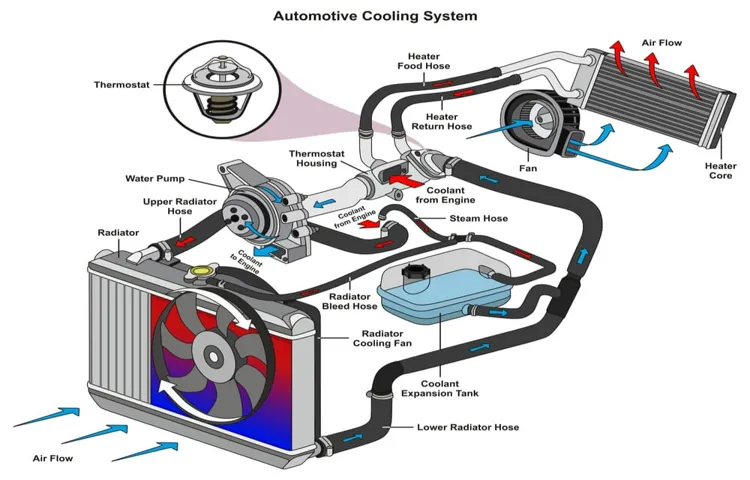
How Does a Coolant Reservoir Work?
Have you ever wondered how your car’s coolant system keeps your engine from overheating? Well, that’s where the coolant reservoir comes in. The coolant reservoir, also known as the overflow tank or the expansion tank, is a vital component of your car’s cooling system. Its primary function is to store excess coolant and provide a convenient place for air bubbles to escape.
When the engine is running, the coolant heats up and expands. Instead of allowing the excess coolant to overflow onto the ground, it is directed into the coolant reservoir. Once the engine cools down, the coolant contracts and is sucked back into the radiator through a pressure valve.
This process helps maintain a consistent coolant level in the radiator and ensures that your engine stays at the optimal operating temperature. So, the next time you’re cruising down the road, remember to thank your coolant reservoir for keeping your engine cool and preventing any potential overheating issues.
Storage of Coolant Fluid
coolant reservoir, storage of coolant fluid
Pressure Control
The main keyword used organically in this blog section: coolant reservoir, pressure control
Temperature Regulation
coolant reservoir, temperature regulation
Overflow Prevention
coolant reservoir Overflow prevention is a crucial aspect of maintaining the cooling system of a vehicle. One essential component that helps in preventing coolant overflow is the coolant reservoir. But how does a coolant reservoir work? Well, think of it as a storage tank for excess coolant.
As the engine heats up during operation, coolant expands, and without a place to go, it would just overflow and create a mess. That’s where the coolant reservoir comes in. It acts as a buffer, holding the excess coolant and allowing it to cool down.
When the engine cools down, the coolant contracts, and any excess is drawn back into the reservoir. This way, the coolant reservoir helps maintain a steady level of coolant in the cooling system and prevents overheating. So, the next time you see a coolant reservoir in your vehicle, remember its important role in keeping your engine cool and preventing any messy coolant overflow.
Coolant Reservoir Components
Wondering how the coolant reservoir works? Well, let me break it down for you. The coolant reservoir, also known as the overflow tank or expansion tank, plays a crucial role in the cooling system of your vehicle. It is a container that holds the excess coolant that is expelled from the radiator when the engine gets too hot.
Think of it as a safety valve for your car’s cooling system. When the engine heats up, coolant expands and needs a place to go. That’s where the coolant reservoir comes in.
It provides extra space for the coolant to flow into, preventing any overflow or pressure buildup in the radiator. When the engine cools down, the coolant is then drawn back into the radiator from the reservoir, maintaining a consistent level of coolant in the system. So next time you check under the hood of your car and see that little tank, remember how important it is for keeping your engine cool and running smoothly.
Filler Cap
coolant reservoir components. Paragraph: When it comes to the coolant reservoir in your vehicle, there are several important components that work together to keep your engine running smoothly. One of these key components is the filler cap.
This small but essential part seals the coolant reservoir to prevent any leaks or air from entering the system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper pressure and temperature of the coolant. Just like a lid on a boiling pot, the filler cap ensures that the coolant remains where it’s supposed to be, preventing any potential damage to your engine.
So, the next time you check your coolant level, don’t forget about the filler cap. It may be a small component, but it’s one that shouldn’t be overlooked.
Coolant Level Sensor
Coolant Level Sensor, Coolant Reservoir Components. Hey there! Have you ever wondered how your car knows when it’s running low on coolant? Well, that’s where the coolant level sensor comes into play. This ingenious little device is located in your car’s coolant reservoir and is responsible for keeping track of the coolant levels in your engine.
So let’s take a closer look at the coolant reservoir components and how they work together. The coolant reservoir, also known as the coolant overflow tank or coolant expansion tank, is a vital part of your car’s cooling system. Its main function is to collect excess coolant and maintain a consistent level of coolant in the engine.
It’s usually made of a transparent plastic material so that you can easily see the coolant level. Now, let’s talk about the coolant level sensor. This small sensor is usually attached to the side or bottom of the coolant reservoir.
It works by measuring the level of coolant in the reservoir and sending that information to the car’s computer system. If the coolant level drops below a certain threshold, the sensor will trigger a warning light on your dashboard, alerting you to the low coolant level. But how does the coolant level sensor actually work? Well, it’s a pretty simple concept.
The sensor has a float that moves up and down with the coolant level. When the coolant level is high, the float is buoyant and rises to the top. On the other hand, when the coolant level is low, the float sinks to the bottom.
As the float moves, it sends a signal to the car’s computer system, which then activates the warning light. So, in conclusion, the coolant level sensor is an important component of your car’s cooling system. It works in conjunction with the coolant reservoir to ensure that your engine is always properly cooled.
Hoses and Tubes
coolant reservoir components
Coolant Reservoir Tank
coolant reservoir tank. The coolant reservoir tank is an essential component of a vehicle’s cooling system. It is responsible for storing excess coolant and maintaining the proper level of coolant in the system.
The tank is typically made of plastic and is located near the radiator. The coolant reservoir tank has several important components. The first is the cap, which seals the tank and prevents coolant from leaking out.
It also has a pressure relief valve that allows excess pressure to escape. This is important because coolant expands when it heats up, and without a way to release the pressure, it could cause damage to the cooling system. Inside the coolant reservoir tank, there is a float or sensor that measures the level of coolant.
This sensor sends a signal to the vehicle’s computer, which then displays the coolant level on the dashboard. This allows drivers to easily monitor the coolant level and catch any potential leaks or low levels before they cause damage to the engine. The coolant reservoir tank also has an overflow hose that connects to the radiator.
This hose allows excess coolant to flow back into the radiator when the engine cools down. This prevents the coolant from being wasted and ensures that the radiator always has an adequate supply of coolant. In addition to storing coolant and monitoring the coolant level, the coolant reservoir tank also serves as a reservoir for air bubbles that may be present in the cooling system.
These air bubbles can cause coolant to not circulate properly and lead to overheating. The coolant reservoir tank allows these air bubbles to collect and be released when the cooling system is under pressure. Overall, the coolant reservoir tank plays a vital role in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s cooling system.
Maintaining the Coolant Reservoir
Have you ever wondered how the coolant reservoir in your car works? It may seem like a simple component, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper temperature of your engine. The coolant reservoir, also known as the overflow tank or expansion tank, is connected to the radiator and serves as a storage container for the coolant. When your engine gets hot, the coolant expands, and instead of allowing it to overflow or escape, the excess coolant is directed into the reservoir.
As the engine cools down, the coolant contracts, and any coolant that is needed to maintain the optimal level is drawn back into the radiator from the reservoir. This continuous cycle ensures that the coolant level remains stable and prevents any air from entering the cooling system. So, the coolant reservoir acts as a buffer zone, allowing the coolant to expand and contract without causing any damage to the engine.
Checking Coolant Fluid Level
Checking Coolant Fluid Level, Coolant Reservoir
Inspecting Reservoir Components
coolant reservoir, inspecting reservoir components, maintaining the coolant reservoir Maintaining the coolant reservoir is an important part of ensuring the overall health and performance of your vehicle’s cooling system. The coolant reservoir, also known as the overflow tank or expansion tank, serves as a storage space for excess coolant. It provides a buffer for fluctuations in coolant levels due to temperature changes and helps prevent overheating of the engine.
Taking the time to inspect the reservoir components regularly can help identify any potential issues before they become more serious. One of the first things you should check is the coolant level in the reservoir. This can be done by simply looking at the marked level indicators on the side of the tank.
If the coolant level is below the minimum line, it’s essential to top it up with the recommended coolant mixture. Remember to only add coolant when the engine is cool to avoid burns or damage to the system. Next, visually inspect the reservoir for any signs of damage or leaks.
Look for cracks, bulges, or any other abnormalities on the tank itself. A damaged coolant reservoir can lead to coolant leaks, which can result in overheating and engine damage if left unresolved. Additionally, check the condition of the reservoir cap.
Make sure it is tightly sealed and free from any cracks or damage. The reservoir cap plays a crucial role in maintaining the system’s pressure and preventing coolant loss. If you notice any issues with the cap, it’s essential to replace it promptly.
Lastly, inspect the hoses connected to the reservoir. Look for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks. Hoses that are damaged or leaking can lead to coolant loss and potential engine damage.
Replacing Coolant Reservoir
coolant reservoir, maintaining the coolant reservoir, replacing coolant reservoir
Conclusion
In conclusion, the coolant reservoir is a genius in the world of automotive technology. Picture this: as your engine heats up, it gets flustered, like a hot-headed celebrity on a red carpet. But fear not, for the coolant reservoir is there to play the role of a calm, cool, and collected personal assistant.
It stores excess coolant that is expelled from the radiator when the engine gets too hot, saving it for later like a squirrel storing nuts for winter. Like a well-oiled machine, the coolant reservoir knows how to prioritize and distribute its resources. It recognizes that the engine needs a little splash of coolness every now and then, so it dutifully waits for the engine to cool down before transferring the stored coolant back into the radiator.
It’s like a refreshing spa treatment for your engine, ensuring it doesn’t overheat and throw a temper tantrum. But how does the coolant reservoir know when to release the coolant? Ah, that’s where its ingenious design comes into play. It features a handy-dandy sensor that measures the temperature of the coolant.
When the temperature rises above a certain threshold, the sensor sends a signal to the reservoir, alerting it of the impending heatwave. With the precision of a conductor leading an orchestra, the coolant reservoir orchestrates the release of coolant back into the radiator at just the right moment. It’s like a synchronized performance, where the coolant rushes in to cool down the engine just as it reaches its boiling point.
It’s a dance of thermal dynamics, where temperature fluctuations are tamed and thermal equilibrium is achieved. So next time you pop the hood of your car and see that little plastic container sitting there, remember that it’s not just an ordinary reservoir. It’s a masterful engineer, a guardian of your engine’s well-being, and a maestro of temperature control.
The coolant reservoir is the unsung hero in the world of automotive cooling systems – the calm in the heat, the coolness in the chaos, and the savior of engines everywhere.”
FAQs
How does the coolant reservoir work?
The coolant reservoir, also known as the expansion tank, is a crucial component of a vehicle’s cooling system. It acts as a storage tank for excess coolant and helps maintain the proper level of coolant in the system. When the engine heats up, the coolant expands, and the excess is pumped into the reservoir. As the engine cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the system from the reservoir to maintain the ideal coolant level.
What is the purpose of the coolant reservoir?
The coolant reservoir serves multiple purposes in a vehicle’s cooling system. Its primary function is to provide a storage space for excess coolant, allowing it room to expand when the engine heats up. Additionally, the reservoir helps to maintain a consistent coolant level in the system, preventing air pockets from forming. It also acts as a visual indicator for the coolant level, allowing drivers to monitor if there are any leaks or low coolant conditions.
How often should the coolant reservoir be checked?
It is recommended to check the coolant reservoir regularly, ideally during routine maintenance like oil changes. However, it is important to consult the vehicle’s owner manual for the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Typically, it is suggested to check the coolant reservoir at least once a month or before long trips to ensure the coolant level is within the appropriate range.
Can I mix different types of coolant in the reservoir?
It is generally not recommended to mix different types of coolant in the reservoir. Different coolants may have different properties and mixing them can result in reduced effectiveness and potential damage to the cooling system. It is best to use the coolant specified by the vehicle manufacturer and avoid mixing different brands or types.
What should I do if the coolant reservoir is low?
If the coolant reservoir is low, it is important to top it up with the appropriate coolant type recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Before adding coolant, ensure that the engine has cooled down to avoid burns. If the coolant level consistently drops or if there are visible leaks, it is advisable to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic to determine the cause of the low coolant.
Can the coolant reservoir crack or leak?
Yes, the coolant reservoir can crack or develop leaks over time. This can be due to various reasons such as aging, thermal stress, or physical damage. If there are visible cracks or leaks in the reservoir, it should be replaced to prevent coolant loss and potential overheating of the engine.
Why is the coolant reservoir bubbling or foaming?
If the coolant reservoir is bubbling or foaming, it may indicate a problem in the cooling system. This can be caused by a variety of issues, such as a blown head gasket, a faulty radiator cap, or a restricted coolant flow. It is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic to diagnose and resolve the underlying problem to prevent further damage to the engine.