Are you curious about how inverters consume power? Understanding the power consumption of inverters can help you make informed decisions when it comes to using these devices. Inverters are essential in converting DC (direct current) power to AC (alternating current) power, enabling us to use appliances and devices that require AC power. But how do inverters themselves consume energy? Let’s dive into the world of inverter power consumption to shed some light on this fascinating topic.
Think of an inverter as a translator. It takes the language of direct current (DC), which is the standard language of batteries and solar panels, and translates it into the language of alternating current (AC), which is the language that our homes and businesses use. Just like how a translator can’t help but use some of their own energy to convey a message, inverters also consume energy in the process.
But how much energy do inverters actually consume? It depends on several factors, including the size and efficiency of the inverter, as well as the load it is powering. Inverters have their own internal consumptions, referred to as “quiescent power” or “no-load power.” This power is used to operate the internal circuits and keep the inverter ready to convert power whenever it’s needed.
The no-load power consumption is typically small, but it can vary between different models and types of inverters. When it comes to powering loads, inverters consume energy proportionate to the power demand of the load. In other words, the more power your devices and appliances require, the more energy the inverter will consume.
It’s important to note that inverters are not 100% efficient, meaning there will always be some energy loss during the conversion process. The efficiency of an inverter is often expressed as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating better efficiency. To understand how power consumption varies, think of a light dimmer switch.
When you turn the switch to its lowest setting, the amount of power consumed by the light bulb is significantly lower compared to when the switch is turned to its highest setting. Similarly, an inverter will consume less power when it is powering light loads, and more power when it is powering heavy loads. In summary, inverters consume power in two main ways – through their own internal operations and through the power demands of the load they are powering.
Table of Contents
What is an Inverter?
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power, allowing you to use your electronic devices and appliances when you don’t have access to a traditional power source. But have you ever wondered how much power an inverter actually consumes? Well, the power consumption of an inverter depends on its size and capacity. Generally, smaller inverters that are used for charging small electronic devices consume less power compared to larger inverters that are used to power larger appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners.
The power consumption is also influenced by the efficiency of the inverter. Higher efficiency inverters consume less power, while lower efficiency inverters consume more power. So, if you’re concerned about power consumption, it’s important to choose an inverter that is the right size for your needs and has a high efficiency rating.
Heading Three
inverter An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) power from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC) power, which is used to power household appliances and electronics. In simple terms, an inverter allows you to use DC power from sources like batteries and solar panels to power AC devices such as televisions, refrigerators, and air conditioning units. Think of an inverter like a language translator.
It takes the energy from the battery or solar panel and translates it into a form that can be understood by your appliances. Just like how a translator converts one language into another, an inverter converts DC power into AC power, which is the language that our electrical devices understand. Inverters come in different sizes and capacities, depending on the power requirements of the appliances you want to connect to them.
Some inverters are small and portable, making them ideal for camping trips or powering small devices. Others are larger and more powerful, capable of providing electricity to an entire home during a power outage. In addition to converting DC to AC power, modern inverters also have advanced features such as surge protection, voltage regulation, and even the ability to connect to Wi-Fi networks for remote monitoring and control.
These features make inverters more efficient and convenient to use. Overall, inverters are essential for harnessing the power of batteries and solar panels, allowing us to make the most out of renewable energy sources. They provide a bridge between the DC power stored in batteries and solar panels and the AC power required to run our everyday appliances.
So next time you turn on your television or charge your phone, remember that there’s an inverter working behind the scenes to make it all possible.

Heading Three
inverter, electricity, power supply, AC/DC, solar panels, battery, backup power Have you ever wondered what an inverter is? Well, an inverter is an essential device that plays a crucial role in our daily lives, especially when it comes to power supply. In simple terms, an inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. So, why is this important? Let me explain.
Most of the electrical appliances we use in our homes, offices, and even on the go, use AC power. However, the power we get from sources like solar panels or batteries is usually DC power. This is where the inverter comes in.
It takes the DC power and converts it into AC power, allowing us to use our devices without any hassle. Furthermore, inverters can also act as a backup power supply during a blackout or when there is no access to the main power grid. They provide uninterrupted power, ensuring that our essential appliances and devices can still function.
So, now you know what an inverter is and why it is an important part of our everyday lives.
Factors Affecting Power Consumption
When it comes to power consumption, inverters can vary based on a number of factors. The type and size of the inverter, as well as the load or devices being powered, can all affect how much power an inverter consumes. In general, larger inverters will consume more power than smaller ones, as they are designed to handle a higher load.
Additionally, the efficiency of the inverter can also play a role in power consumption. Some inverters are designed to be more energy-efficient, meaning they will consume less power overall. However, it’s important to keep in mind that even the most efficient inverters will still use some power.
Ultimately, the amount of power an inverter consumes will depend on a variety of factors, so it’s important to consider these factors when choosing an inverter for your specific needs.
Efficiency of the Inverter
The efficiency of the inverter is a crucial aspect to consider when it comes to power consumption. Several factors can affect the efficiency of an inverter, ultimately impacting how much power it consumes. One of the key factors is the load connected to the inverter.
Inverters operate best when the load matches their rated capacity. If the load is too small, the inverter may operate at a lower efficiency level which can result in higher power consumption. On the other hand, if the load is too large, the inverter may struggle to meet the demands, leading to a decrease in efficiency and potentially higher power consumption as well.
Another factor that can affect the efficiency of an inverter is the quality of its components. A well-built inverter with high-quality components will generally have a higher efficiency rating compared to a lower-quality one. Additionally, the age and condition of the inverter can also play a role in its efficiency.
Over time, the internal components of an inverter can deteriorate, leading to a decrease in efficiency and potentially increased power consumption. It is worth considering regular maintenance and replacing old inverters to maintain optimal efficiency levels. By taking these factors into consideration, it is possible to choose an inverter that is both efficient and power-saving.
Load Capacity of the Inverter
load capacity of the inverter, power consumption, factors affecting, burstiness
Type of Inverter
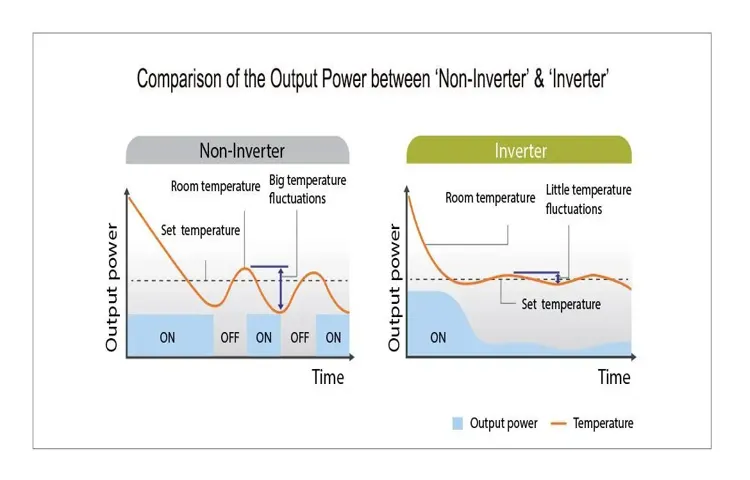
The type of inverter you choose can have a significant impact on power consumption. There are two main types of inverters: modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Modified sine wave inverters are the more affordable option, but they can also be less efficient.
They are suitable for most household appliances, but they may cause some electronics to run less efficiently or make a buzzing sound. On the other hand, pure sine wave inverters produce a smoother and cleaner wave, similar to the power you get from the utility grid. This makes them more expensive but also more efficient.
They are suitable for sensitive electronics like laptops, televisions, and medical equipment. So, when choosing an inverter, it’s essential to consider the type that best suits your power needs and the devices you will be using.
Calculating Power Consumption
Have you ever wondered how much power an inverter consumes? Well, it depends on several factors. The power consumption of an inverter varies based on its capacity, the load it is connected to, and the efficiency of the inverter itself. Inverters are designed to convert DC (direct current) power from a battery or solar panel into AC (alternating current) power for powering appliances and electronics.
The power consumption of an inverter can range from a few watts to several hundred watts. Higher capacity inverters generally consume more power than lower capacity ones. Additionally, the power consumption increases as the load connected to the inverter increases.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of the inverter plays a significant role in its power consumption. More efficient inverters tend to consume less power as they convert energy more effectively. So, if you’re looking to minimize power consumption, it’s advisable to choose a smaller capacity inverter and opt for a more efficient model.
Formula for Power Consumption
power consumption, calculating power consumption
Example Calculation
power consumption
Tips for Reducing Power Consumption
Have you ever wondered how much power an inverter actually consumes? Well, the answer can vary depending on various factors such as the size and efficiency of the inverter, as well as the load it is powering. In general, inverters consume a small amount of power themselves, usually around 10-20% of the total power being used by the connected devices. This means that if you have an inverter with a capacity of 1000 watts and are using devices that require a total of 500 watts, the inverter itself may consume around 50-100 watts.
However, it’s important to note that this is just a rough estimate and actual power consumption can vary. To reduce power consumption, you can consider investing in a more efficient inverter or properly sizing your inverter to match the load requirements. Additionally, you can use energy-efficient devices and turn off any unnecessary appliances or devices when not in use to further reduce power consumption.
Choosing a High-Efficiency Inverter
Tips for Reducing Power Consumption When it comes to reducing power consumption, choosing a high-efficiency inverter is a smart choice. An inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) power into AC (alternating current) power, allowing you to use DC power sources like solar panels to power your AC appliances. By opting for a high-efficiency inverter, you can ensure that your power conversion process is as efficient as possible, minimizing energy waste and reducing your overall power consumption.
One tip for choosing a high-efficiency inverter is to look for a model that has a high efficiency rating. Efficiency ratings indicate how much of the DC power that the inverter receives is converted into AC power. The higher the efficiency rating, the less energy is lost during the conversion process.
Look for inverters with efficiency ratings above 90% for the best energy savings. Another tip is to consider the power output of the inverter. Choose an inverter that has a power output that matches your energy needs.
Too large of an inverter can result in wasted energy, while too small of an inverter may not be able to power all of your appliances efficiently. Take into account the wattage requirements of your appliances and choose an inverter that can handle the load without excessive energy loss. Additionally, consider the type of inverter you want to use.
There are three main types: string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are the most commonly used and are suitable for most residential and commercial applications. Microinverters and power optimizers, on the other hand, are more suitable for systems with shaded or complex configurations.
Choosing the right type of inverter for your specific needs can help optimize energy efficiency and reduce power consumption. In conclusion, reducing power consumption can be achieved by choosing a high-efficiency inverter. Look for inverters with high efficiency ratings, consider the power output and choose the right type of inverter for your needs.
Proper Sizing of Inverter
power consumption, inverter size
Reducing Standby Power
Reducing Standby Power When it comes to reducing power consumption, one area that often gets overlooked is standby power. Standby power is the energy used by electronic devices when they are not in use but still plugged in. While it may not seem like a lot, standby power can account for a significant portion of your energy bill.
Luckily, there are several tips you can follow to minimize standby power and save money. First, consider using power strips to easily turn off multiple devices at once. This way, you can completely cut off power to devices like your TV, computer, or gaming console when you’re not using them.
Additionally, look for devices that have low standby power consumption. Smart power strips and energy-efficient appliances are designed to minimize standby power and can make a big difference in your overall energy usage. Finally, don’t forget to unplug chargers and other devices when they’re not in use.
Even when a device is not actively charging, it can still use power if it’s plugged in. By implementing these simple tips, you can reduce standby power and lower your energy bill while helping to protect the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the power consumption of an inverter can be a perplexing and elusive subject. Just like a magician’s tricks, it can leave us scratching our heads in wonderment. But fear not, for I am here to unravel the enigma and shed light on the matter.
You see, an inverter is like the chameleon of the electrical world. It takes on the role of a transformer, transforming DC power into AC power, and then masquerades as an electrician, supplying energy to our beloved appliances. But just like any adept impersonator, there is always a secret cost to maintaining the facade.
When an inverter converts power from DC to AC, it must deal with the inevitable losses that occur during the process. These losses, my friends, are like tiny energy bandits that pilfer a fraction of the power being converted. They are the sneaky pickpockets of the electrical universe, snatching away a portion of the energy without us even realizing it.
The amount of power consumed by an inverter depends on a variety of factors, such as its efficiency rating and the load it is powering. Think of it as a high-stakes poker game, where the inverter’s efficiency rating is its poker face, hiding the true power consumption behind a cunning smile. The higher the efficiency rating, the less power it guzzles; but be warned, a low-efficiency inverter can drain your energy resources faster than a vampire at a blood bank.
So, how much power does an inverter really consume, you may ask? Well, my dear reader, it is a conundrum wrapped in an enigma, disguised as a riddle. The answer lies in the intricacies of electrical engineering, where calculations and formulas dance a tango with power ratings and efficiency coefficients. In the end, it all boils down to this: an inverter consumes power, but with the right knowledge and careful selection, you can minimize its impact on your energy bill.
So, when faced with the question of how much power an inverter consumes, remember this clever quip: it’s not about the power the inverter consumes, but the power of knowledge you possess to make an informed choice. Happy powering, my friends!”
FAQs
How much power does a typical inverter consume?
The power consumption of a typical inverter depends on its size and the load it is powering. On average, a small inverter may consume around 10-50 watts, while a larger inverter may consume around 100-500 watts.
What factors affect the power consumption of an inverter?
The power consumption of an inverter can be influenced by factors such as the size and efficiency of the inverter, the type and number of appliances connected to it, and the duration of use.
How can I calculate the power consumption of an inverter?
To calculate the power consumption of an inverter, you need to multiply the rated power of the inverter (in watts) by the number of hours it is used. For example, if you have a 200-watt inverter and you use it for 5 hours, the power consumption would be 200 watts * 5 hours = 1000 watt-hours (or 1 kilowatt-hour).
Are there any energy-efficient inverters available in the market?
Yes, there are energy-efficient inverters available in the market. Look for inverters with higher efficiency ratings, such as those labeled with Energy Star certification. These inverters are designed to minimize power losses and reduce overall energy consumption.
Can I reduce the power consumption of an inverter?
Yes, you can reduce the power consumption of an inverter by using it efficiently. Avoid using oversized inverters for small loads, as they tend to have higher standby power consumption. Also, consider investing in inverters with power saving features, such as automatic shutdown when not in use.
How does the load connected to an inverter affect its power consumption?
The power consumption of an inverter is directly proportional to the load it is powering. If you connect a high-power appliance, such as an air conditioner, to the inverter, it will consume more power compared to a low-power appliance like a fan or a few LED lights.
Is there a difference in power consumption between modified sine wave and pure sine wave inverters?
Yes, there can be a slight difference in power consumption between modified sine wave and pure sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters are generally more efficient, resulting in lower power consumption compared to modified sine wave inverters.
Can a solar inverter consume less power than a regular inverter? A8. Yes, a solar inverter can consume less power than a regular inverter, especially when using solar energy as the primary source of power. Solar inverters are designed to optimize the conversion of solar energy into usable electricity, resulting in lower overall power consumption.
How does the size of an inverter affect its power consumption?
In general, larger inverters have higher power consumption compared to smaller inverters. This is because larger inverters are typically designed to handle larger loads and may have more internal components that require power.
Are there any standby power losses associated with inverters?
Yes, there can be standby power losses associated with inverters, especially if they have power-saving features or if they are left connected to a power source without any load. It is recommended to disconnect the inverter from the power source when not in use to minimize standby power consumption.
Can the power consumption of an inverter fluctuate?
Yes, the power consumption of an inverter can fluctuate depending on the variation in load or the efficiency of the inverter. For example, if the load connected to the inverter varies, the power consumption will also vary accordingly.
How can I monitor the power consumption of an inverter?
You can monitor the power consumption of an inverter by using a power meter or a wattmeter. These devices can measure the actual power consumed by the inverter and help you understand its efficiency and performance.