Hey there! Are you looking for a captivating introduction to this blog post? Well, look no further because I’ve got you covered! In this blog post, we’re going to dive deep into the topic of “Introduction.” Now, you might be wondering, what exactly is an introduction and why is it so important? Picture this – you’re at a party, and you walk into a room full of strangers. What’s the first thing you do? You introduce yourself, right? Well, the same concept applies to blog posts.
The introduction sets the tone and grabs the reader’s attention right from the start, making it a crucial part of any piece of writing. So, let’s explore the ins and outs of crafting the perfect introduction together, shall we?
Table of Contents
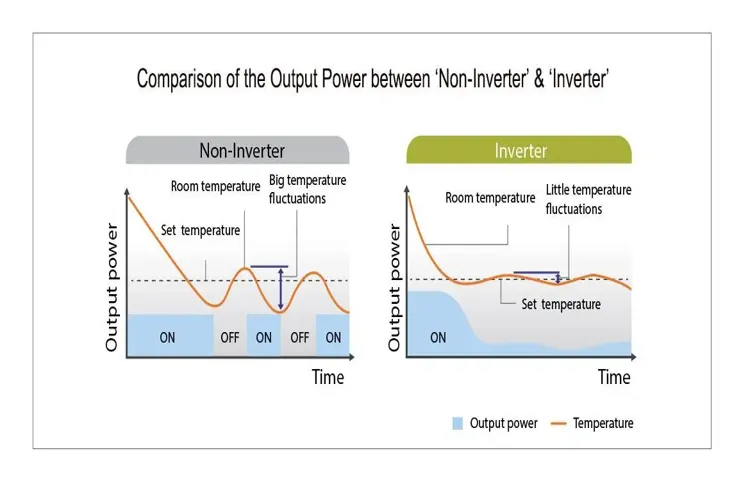
What is an inverter?
When it comes to inverters, one question that often pops up is, “How much power does an inverter consume?” Well, the answer to that question depends on several factors. Firstly, the power consumption of an inverter can vary depending on its size and efficiency. Larger inverters generally consume more power than smaller ones.
Additionally, the efficiency of the inverter plays a significant role in its power consumption. More efficient inverters convert a higher percentage of the power they receive, resulting in lower power consumption. Another factor that determines the power consumption of an inverter is the load that it is powering.
Different appliances have different power requirements, so the power consumption will vary accordingly. Additionally, the duration for which the inverter is in use also affects its power consumption. Generally, inverters consume power even when they are not actively powering any appliances.
Therefore, it is important to choose an inverter that matches your power needs and is energy-efficient to minimize power consumption.
How does an inverter work?
When it comes to the power consumption of an inverter, it really depends on the size and efficiency of the device. Inverters work by converting direct current (DC) from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC) that is used to power our everyday appliances. During this conversion process, there is a small amount of power loss due to the internal components and electrical resistance.
However, modern inverters are designed to be highly efficient, with conversion efficiency rates ranging from 80% to 95%. This means that for every 100 watts of DC power input, the inverter will produce between 80 to 95 watts of AC power output. So, while inverters do consume some power, the amount is relatively small compared to the power they provide.
Additionally, the actual power consumption of an inverter will also depend on the load connected to it. A higher load will require more power from the inverter, resulting in slightly higher power consumption.

Power consumption of inverters
Have you ever wondered how much power an inverter consumes? Well, the power consumption of inverters can vary depending on their size and the amount of load they are supporting. On average, a small inverter that is used to power a few electronic devices can consume around 10-50 watts of power. However, larger inverters that are used to power heavy loads like refrigerators and air conditioners can consume anywhere from 500-1500 watts of power.
It’s important to keep in mind that the power consumption of an inverter is not constant and can fluctuate depending on the demand for power. So, if you’re thinking about getting an inverter, it’s a good idea to assess your power needs and choose one that is suitable for your requirements.
Factors affecting power consumption
Power consumption of inverters can be affected by several factors. One of the primary factors is the load that the inverter is powering. Higher loads require more power, resulting in increased power consumption.
Another factor is the efficiency of the inverter itself. Inverters with higher efficiency ratings will use less power to convert DC power to AC power. The design and quality of the inverter can also impact power consumption.
Inverters that are poorly designed or made with low-quality components may consume more power than their more well-built counterparts. Additionally, the operating conditions of the inverter can affect power consumption. For example, inverters operating in high ambient temperatures may consume more power due to increased internal losses.
It’s important to consider these factors when choosing an inverter to ensure optimal power consumption and efficiency.
Calculating power consumption
power consumption of inverters
Examples of power consumption
“Inverters play a crucial role in many household appliances and electronic devices, but have you ever wondered about their power consumption? Let’s dive into it! The power consumption of inverters can vary depending on several factors such as the size and capacity of the inverter, as well as the specific device or appliance it is powering. Inverters convert DC power to AC power, and in doing so, they draw power from a DC source such as a battery or solar panel. The efficiency of the inverter also affects its power consumption, with higher efficiency inverters using less power.
Additionally, the power load being operated by the inverter can impact its energy usage. For example, a smaller appliance may require less power from the inverter compared to a larger device. Overall, understanding the power consumption of inverters is important for efficient energy management and ensuring that your devices operate optimally.
“
Choosing an efficient inverter
Inverter is an important component in a solar power system as it converts direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power appliances and devices in our homes. One common concern people have is how much power an inverter itself consumes. The power consumption of an inverter depends on its efficiency rating.
Inverters with higher efficiency ratings consume less power while converting DC to AC. For example, an inverter with a 95% efficiency rating will waste only 5% of the power during the conversion process, while an inverter with an 85% efficiency rating will waste 15% of the power. It’s important to choose an inverter with a high efficiency rating to minimize power loss and maximize the overall efficiency of the solar power system.
Choosing an efficient inverter can help reduce electricity bills and make the system more eco-friendly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the power consumed by an inverter is like a stealthy ninja, silently sipping energy from the shadows. Its consumption is as elusive as a magician’s trick, vanishing into thin air while leaving behind only the bewilderment of the onlooker. Like a mischievous pixie, the inverter cunningly disguises its power consumption, blending seamlessly into the background noise of our daily lives.
So, the next time you wonder about the power consumed by an inverter, remember that it is an enigma, a puzzle waiting to be solved. But fear not, for with a little bit of wit and wisdom, you too can unravel the mystery of the inverter’s power consumption. Happy sleuthing!”
FAQs
How much power does an inverter consume when idle?
When an inverter is idle or not actively powering any devices, it still consumes a small amount of power. This standby power consumption is typically around 1-5 watts.
Does the power consumption of an inverter depend on its size?
Yes, the power consumption of an inverter can depend on its size. Generally, larger inverters have a higher idle power consumption compared to smaller ones. However, this difference is not significant and may vary depending on the specific model and brand.
Can the power consumption of an inverter be reduced?
Yes, there are a few ways to reduce the power consumption of an inverter. One way is to choose an inverter with a low idle power rating. Additionally, turning off the inverter when not in use or using a power-saving mode if available can also help reduce its power consumption.
Does the type of load connected to an inverter affect its power consumption?
Yes, the type of load connected to an inverter can affect its power consumption. Some devices may have a higher power demand, causing the inverter to draw more power. It’s important to check the power requirements of the devices you plan to connect to the inverter to ensure it can handle the load efficiently.
Can the power consumption of an inverter vary based on its efficiency?
Yes, the efficiency of an inverter can affect its power consumption. Inverters with higher efficiency tend to consume less power as they convert the energy more effectively. It’s recommended to choose an inverter with a high efficiency rating to minimize power wastage.
Do inverters consume power even when no devices are connected?
Yes, inverters can consume power even when no devices are connected. This is because an inverter needs to maintain its standby power to be ready for immediate use when devices are connected and turned on.
Are there any energy-saving features in modern inverters?
Yes, some modern inverters come with energy-saving features. These features can include automatic power-down when no devices are connected, power-saving modes, and advanced power management systems. These features help optimize power consumption and reduce energy wastage.