Have you ever wondered how to determine the size of a power inverter? Whether you’re considering installing one in your vehicle, RV, boat, or home, it’s important to choose the right size to meet your needs. A power inverter allows you to convert the DC (direct current) power from your battery into AC (alternating current) power, which is what most household appliances and electronics use. But finding the right size can be a bit overwhelming if you’re not familiar with the technical aspects.
It’s like trying to find the perfect pair of shoes – you want them to fit just right, not too big or too small. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the factors you need to consider when determining the size of a power inverter, so you can confidently choose the best one for your needs.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Are you considering getting a power inverter but not sure what size you need? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! Choosing the right size power inverter can be a bit confusing, but it’s important to get it right to ensure optimal performance. The size of the power inverter you need depends on a few factors, including the power requirements of the devices you plan to connect to it. To determine the size, you’ll need to consider the wattage of each device and add them up to get the total wattage required.
For example, if you plan to power a laptop (60W) and a small refrigerator (100W), you would need a power inverter with a minimum of 160W. It’s always a good idea to choose an inverter with a slightly higher wattage capacity to accommodate any power surges or unexpected increases in power demand. So don’t fret, with a little bit of calculation, you’ll be able to determine the right size power inverter for your needs.
Explanation of Power Inverters
power inverters, inverters, electricity, DC to AC conversion, solar power, car battery, backup power, portable power
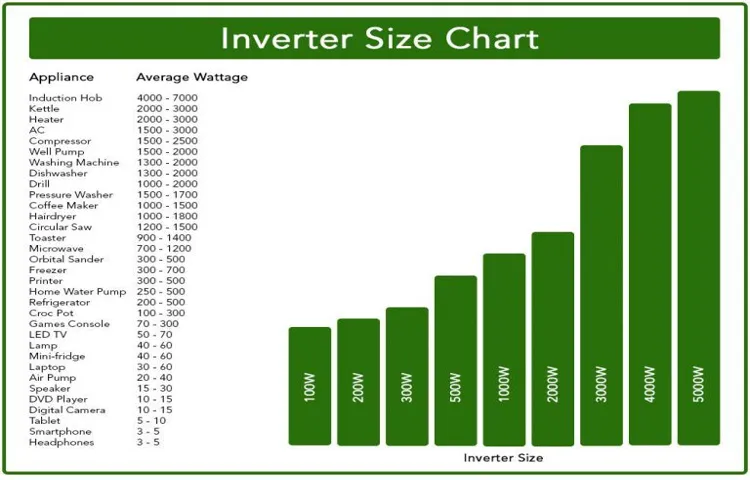
Factors to Consider
When it comes to choosing the right size power inverter, there are a few factors you need to consider. First and foremost, you need to determine the total power consumption of the devices you plan to connect to the inverter. This can usually be found on the device’s specifications or label.
Once you have this information, you’ll need to add up the power consumption of all the devices to get the total wattage. Next, you’ll want to consider the surge or peak power requirements of your devices. Some devices, like refrigerators or power tools, require a higher initial surge of power when they start up.
It’s important to choose an inverter that can handle this surge power without overloading. You’ll also need to think about the continuous power rating of the inverter. This is the amount of power that the inverter can provide consistently over time.
It’s important to choose an inverter that has a continuous power rating higher than the total wattage of the devices you plan to connect. Lastly, you’ll want to consider any future power needs. If you think you might be adding more devices or appliances in the future, it’s a good idea to choose an inverter with a higher power rating to accommodate these potential additions.
Overall, choosing the right size power inverter involves considering the total power consumption, surge power requirements, continuous power rating, and future power needs. Taking these factors into account will help ensure that you choose an inverter that can effectively power your devices without any issues.
Power Consumption of Devices
power consumption, devices
Number of Devices
“Factors to Consider When Choosing the Number of Devices for Your Home” When it comes to deciding how many devices you need for your home, there are several factors to consider. First, think about how many people will be using the devices. If you have a large family or frequently have guests over, you’ll likely need more devices to accommodate everyone.
Additionally, consider the types of devices you’ll be using. If you enjoy streaming movies and TV shows, you may want to have multiple devices to ensure smooth playback. On the other hand, if you primarily use your devices for browsing the internet or checking emails, you might not need as many.
Another important factor is the size of your home. If you have a small apartment, you may only need a couple of devices to provide coverage throughout the space. However, if you have a large house with multiple floors and rooms, you’ll likely need more devices to ensure that every corner of your home has a strong Wi-Fi signal.
Lastly, think about your budget. The more devices you have, the more expensive it can be. You’ll not only need to purchase the devices themselves but also potentially upgrade your internet plan to accommodate the increased usage.
It’s important to find a balance between having enough devices to meet your needs and staying within your budget. In conclusion, when choosing the number of devices for your home, consider factors such as the number of users, the types of devices and their intended use, the size of your home, and your budget. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure that you have the right number of devices to meet your needs without overspending.
Type of Inverter
inverter, factors to consider, type of inverter When it comes to choosing an inverter, there are several factors to consider that will help you make the right decision for your specific needs. One of the first factors to think about is the type of inverter you need. There are several different types available, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers.
String inverters are the most common type and are typically used in larger solar installations. They are connected to multiple solar panels in series and convert the DC power generated by the panels into AC power. Microinverters, on the other hand, are installed on each individual solar panel.
This means that each panel operates independently, which can be beneficial if you have shading issues or panels installed at different angles. Power optimizers are another type of inverter that can be used in conjunction with string inverters or microinverters. They are installed on each panel, similar to microinverters, but work to optimize the output of each panel.
This can be particularly useful if you have panels that are exposed to shading or are installed at different orientations. When considering the type of inverter you need, it’s important to think about factors such as the size of your solar installation, the amount of shading you have, and your budget. String inverters are often more cost-effective for larger installations, while microinverters and power optimizers may be a better choice for smaller installations with shading issues.
Overall, the type of inverter you choose will depend on your specific needs and preferences. By considering factors such as the size of your installation, shading, and budget, you can make an informed decision that will help you get the most out of your solar panels.
Efficiency of Inverter
Efficiency of Inverter When considering the efficiency of an inverter, there are several factors that need to be taken into account. One of the main factors is the type of inverter being used. There are various types of inverters available, such as sine wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters, and square wave inverters.
Sine wave inverters are known to have the highest efficiency, typically ranging from 85% to 95%, while modified sine wave inverters have a lower efficiency, usually ranging from 60% to 85%. Square wave inverters, on the other hand, have the lowest efficiency, usually below 60%. Another factor that affects the efficiency of an inverter is its load.
Different loads require different amounts of power, and the efficiency of the inverter can vary depending on the load being used. It is important to choose an inverter that is appropriately sized for the load it will be powering in order to achieve the highest efficiency. The input voltage of the inverter also plays a role in its efficiency.
In general, inverters tend to be more efficient when the input voltage is closer to their nominal voltage. For example, if the nominal voltage of the inverter is 12V, it will be most efficient when the input voltage is around 12V. If the input voltage is significantly higher or lower than the nominal voltage, the efficiency of the inverter may decrease.
The quality of the inverter also affects its efficiency. Inverters that are made with high-quality components and designed with efficiency in mind are likely to have higher efficiency than lower-quality inverters. It is important to choose an inverter from a reputable manufacturer that is known for producing high-quality products.
In conclusion, when it comes to the efficiency of an inverter, there are several factors that need to be considered. These include the type of inverter, the load being used, the input voltage, and the quality of the inverter. By taking these factors into account, it is possible to choose an inverter that will provide the highest efficiency and meet the power needs effectively.
Peak Power vs Continuous Power
peak power, continuous power, factors to consider
Calculating the Size
When it comes to choosing the right power inverter for your needs, one of the most important factors to consider is the size. Determining what size power inverter you need is crucial in ensuring that it will be able to handle the power requirements of your devices or appliances. To calculate the size of the power inverter you need, you first need to determine the total wattage of the devices or appliances you plan to power.
This can usually be found on the label or in the user manual of each device. Once you have gathered the wattage information, add up the total wattage of all the devices you plan to power simultaneously. It’s important to note that power inverters are typically rated in terms of their continuous power output.
This means that the inverter should be able to handle the total wattage of the devices you plan to power without exceeding its continuous power rating. Additionally, it’s a good idea to choose a power inverter with a higher wattage rating than the total wattage of your devices to ensure you have some room for future additions or power surges during startup. By taking into account the total wattage of your devices and considering future power needs, you can determine the appropriate size power inverter for your specific requirements.
Step 1: Determine the total wattage
calculating the size, total wattage. One of the first steps to properly sizing your solar system is to determine the total wattage you will need. This is crucial because it determines the size of the solar panels and the capacity of the battery bank that you will require.
To calculate the total wattage, you will need to take into consideration the energy consumption of all the appliances and devices that you will be running on solar power. Start by making a list of all the electrical loads that you will be using, including lights, fans, refrigerator, TV, and any other appliances. Next, find the wattage rating for each of these devices.
This information can usually be found on the manufacturer’s label or in the user manual. Once you have the wattage ratings for all your devices, add them up to get the total wattage. This will give you a rough estimate of the size of the solar system you will need to meet your energy needs.
Step 2: Consider the Surge Power
calculating the size, surge power, generator In order to determine the appropriate size of a generator, it is essential to consider the surge power. Surge power refers to the increased demand for electricity that occurs when certain appliances or equipment start up. This surge can be significantly higher than the normal power requirements of the appliances, and if not accounted for, can overload a generator and cause it to shut down.
Calculating the size of a generator involves taking into account the surge power of the appliances or equipment that will be running off of it. To do this, it is important to determine the starting wattage of each appliance. This information can usually be found on the equipment’s spec sheet or label.
Once you have the starting wattage for each appliance, you will need to add them all up to get the total surge power. This will give you an idea of the maximum amount of power that your generator will need to be able to supply. It is also worth considering the sequence of starting up appliances.
For example, if you plan to start a refrigerator and an air conditioner at the same time, you may need to account for the surge power of both appliances running simultaneously. By accurately calculating the surge power of your appliances and equipment, you can ensure that you choose a generator that is capable of meeting your power needs without overloading. This will help to prevent any unexpected shutdowns or damage to your generator.
So, take the time to consider the surge power when selecting the size of your generator.
Step 3: Determine the size based on your needs
When determining the size of your storage unit, it’s important to consider your specific needs. Calculating the size involves more than just guessing or estimating how much space you’ll need. Instead, it’s important to take a careful inventory of the items you plan to store and consider their size, shape, and specific storage requirements.
This will help you choose the right size storage unit to accommodate your belongings. Start by creating a list of all the items you plan to store. Include measurements or dimensions if possible, as this will be helpful in determining the amount of space you’ll need.
Consider the shape of your items as well. If you have large furniture pieces that cannot be disassembled, you’ll need to account for their size when choosing a unit. Next, think about any special storage requirements your items might have.
For example, if you’re storing sensitive electronics or artwork, you may need climate-controlled storage to protect them from temperature or humidity fluctuations. In this case, you’ll need to select a larger unit to accommodate the extra equipment required for climate control. Consider how frequently you’ll need to access your stored items.
If you plan to regularly retrieve items from your unit, you may want to choose a larger unit to allow for easy access and organization. On the other hand, if you don’t anticipate needing to access your belongings often, a smaller unit may suffice. Finally, factor in any potential future storage needs.
If you think you may need additional storage space in the future, it’s a good idea to choose a slightly larger unit now to allow for future growth. This will save you the hassle and cost of having to move your items to a larger unit later on. By carefully considering your specific needs and taking into account the size, shape, and storage requirements of your items, you can determine the right size storage unit for you.
Examples of Inverter Sizes
“What size power inverter do I need?” is a common question among those looking to power their appliances or devices when they’re away from traditional power sources. The answer to this question depends on the specific appliances or devices you plan to power and their power requirements. Inverter sizes are typically measured in watts, and the size you need will depend on the total wattage of the appliances or devices you want to use.
For example, if you want to power a laptop (around 50 watts) and a small television (around 100 watts), you would need an inverter with a capacity of at least 150 watts. However, it’s always a good idea to choose an inverter with a slightly higher wattage capacity than your highest-rated appliance to ensure it won’t be overloaded. Additionally, you should consider any potential surge currents that may occur when starting certain appliances, as these can temporarily require more power than their rated wattage.
Ultimately, it’s important to do your research and carefully calculate the power requirements of your appliances or devices before choosing the size of your inverter.
Example 1: Powering a Laptop and a Smartphone
When it comes to choosing the right inverter to power your laptop and smartphone, it’s important to consider the size of the inverter. The size of an inverter refers to its power output, measured in watts. Different devices have different power requirements, so it’s crucial to select an inverter that can handle the power needs of both your laptop and smartphone.
For example, a typical laptop consumes around 60-100 watts of power, while a smartphone usually requires about 5-10 watts. So, to power both devices simultaneously, you would need an inverter with a minimum power output of 70-110 watts. When looking at inverter sizes, it’s also important to consider the surge capacity.
Surge capacity refers to the ability of the inverter to handle temporary power spikes when devices are turned on or operating at full capacity. Laptops and smartphones can have sudden power surges, especially during start-up or when performing resource-intensive tasks. To ensure a smooth power supply and prevent any damage to your devices, it’s recommended to choose an inverter with a surge capacity of at least 20-30% above the maximum power output required.
In summary, when choosing an inverter to power your laptop and smartphone, it’s crucial to consider the size of the inverter in terms of its power output. Select an inverter with a power output that can handle the combined power requirements of your laptop and smartphone. Additionally, ensure that the inverter has a surge capacity that can handle any temporary power spikes.
By choosing the right inverter size, you can effectively power your laptop and smartphone without any interruptions or damage to your devices.
Example 2: Powering a Microwave and a Refrigerator
When it comes to powering multiple appliances with an inverter, it’s important to choose the right size to ensure efficient performance. Let’s take the example of a microwave and a refrigerator. These two appliances have different power requirements and it’s vital to have an inverter that can handle both of them simultaneously.
For a typical household microwave, the power consumption can range from 600 to 1200 watts. On the other hand, a refrigerator may consume around 100 to 800 watts depending on its size and efficiency. To power both appliances, you would need an inverter with a continuous output of at least 2000 watts.
This ensures that it can handle the peak power demands of the microwave while still providing enough power for the refrigerator to function properly. Additionally, it’s important to consider the surge power capability of the inverter, which refers to its ability to handle initial power surges when the appliances are turned on. This surge power requirement can be significantly higher than the continuous power and should also be taken into account when choosing an inverter.
Having an inverter that is adequately sized for your appliances will not only ensure smooth operation but also protect your appliances from potential damage due to voltage fluctuations. It’s always a good idea to consult with a professional or refer to the appliance’s specifications to determine the exact power requirements before selecting an inverter.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining the size of power inverter you need is a task that requires a little bit of math and a whole lot of electrical savvy. It’s like finding the perfect French fry to ketchup ratio – too little and you’re left unsatisfied, too much and you risk a mess. So, just like adding enough ketchup to make your fries pop, you want to find an inverter that perfectly matches your power needs without going overboard.
Remember, it’s all about finding that sweet spot of electrical efficiency and fried-potato bliss. So go forth, power up, and let the inverter do its magic – just don’t forget to save some fries for the rest of us.”
Choosing the Right Size Inverter
inverters, inverter sizes, choosing the right size inverter, examples of inverter sizes
Safety Tips and Recommendations
safety tips and recommendations, inverter sizes, inverters Inverters are a useful tool for converting DC power into AC power, but when it comes to using them, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some safety tips and recommendations to keep in mind when using inverters. First and foremost, always read the manufacturer’s instructions and follow them carefully.
This will ensure that you are using the inverter correctly and avoiding any potential hazards. Secondly, make sure that the inverter is properly grounded. Grounding is essential for preventing electric shocks and other electrical accidents.
Additionally, it’s important to keep the inverter in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating. Inverters can generate a lot of heat, and if they are not properly cooled, they can become a fire hazard. It’s also a good idea to regularly inspect the inverter for any signs of damage or wear and tear.
If you notice any issues, such as frayed wires or a damaged casing, it’s important to have the inverter repaired or replaced immediately. Lastly, always be mindful of the inverter’s capacity. Different inverters have different power ratings, and using an inverter that is too small for your needs can overload the system and cause damage.
On the other hand, using an inverter that is too large can also be problematic, as it can waste energy and potentially create electrical malfunctions.
FAQs
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) power from a battery into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to run various electronic devices.
How does a power inverter work?
A power inverter works by using electronic components to convert the low voltage DC power from a battery into the higher voltage AC power that is required to run electronic devices. It typically involves techniques such as pulse width modulation (PWM) or sine wave inversion.
What are the different types of power inverters?
There are three main types of power inverters: modified sine wave inverters, pure sine wave inverters, and square wave inverters. Modified sine wave inverters are the most common and least expensive, but they may not be suitable for all devices. Pure sine wave inverters produce a clean and stable power output, making them suitable for sensitive electronics. Square wave inverters are the most basic type and are typically used for simple appliances.
How do I determine the size of a power inverter I need?
To determine the size of a power inverter you need, you should consider the wattage or power rating of the devices you want to run. Add up the wattage of all the devices you want to power simultaneously, and choose an inverter with a power rating that is equal to or greater than the total wattage.
Can a power inverter drain my battery?
Yes, using a power inverter can drain your battery, especially if you are running high-power devices for an extended period of time. It is important to make sure your battery can handle the load and to monitor its voltage to avoid draining it too much.
Can I run a refrigerator or air conditioner on a power inverter?
Running a refrigerator or air conditioner on a power inverter can be challenging because these devices have high starting currents and require a lot of power. You would need a high-capacity inverter and a large battery bank to handle the load. It is recommended to consult with a professional to determine if it is feasible in your specific situation.
Can I connect multiple batteries to a power inverter to increase the power capacity?
Yes, you can connect multiple batteries in parallel to increase the power capacity of a power inverter. This is often done in applications where more power is needed or longer run times are required. However, it is important to ensure that the batteries are of the same type, size, and voltage to prevent damage to the inverter and batteries.
Can a power inverter be used in a vehicle? A8. Yes, power inverters can be used in vehicles to convert the DC power from the vehicle’s battery into AC power that can be used to run various devices. They are commonly used for powering laptops, phones, and other electronics while on the road.
Are power inverters safe to use?
Power inverters are generally safe to use as long as they are installed and used properly. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions, use the appropriate gauge wiring, and ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating. It is also important to use inverters that have built-in safety features such as overload protection and low voltage alarm/shutdown.
Can a power inverter be used with solar panels?
Yes, power inverters can be used with solar panels to convert the DC power generated by the panels into AC power that can be used in homes or businesses. These inverters are known as grid-tied or grid-connected inverters, and they allow excess power to be fed back into the utility grid, reducing energy costs.


