Welcome to our blog! In this post, we will be diving into the exciting world of introductions. Whether you’re writing an essay, starting a conversation, or presenting a new concept, the introduction sets the tone for what’s to come. It’s your chance to grab your reader’s attention and make a lasting impression.
But what makes a good introduction? How can you captivate your audience and keep them engaged? Get ready to learn some tips and tricks as we explore the art of introductions. So, let’s jump right in and discover how to make a strong first impression!
Table of Contents
What is an inverter?
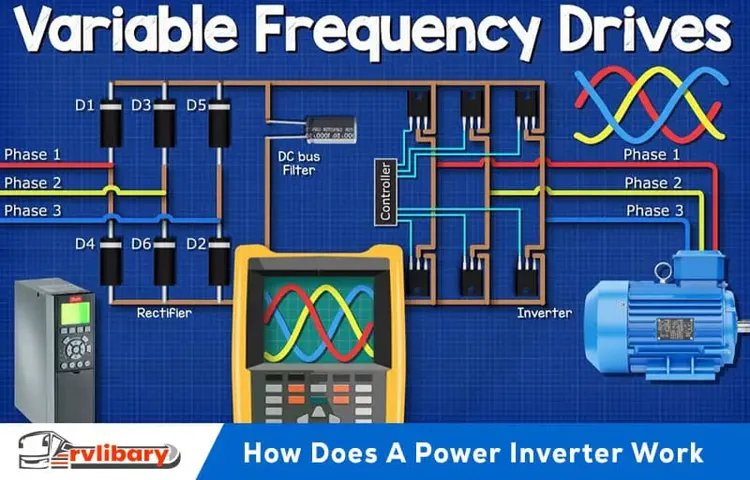
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. This means it takes power from a DC source, such as a battery or solar panels, and converts it into AC power that can be used to run household appliances or other AC devices. So, where does an inverter get its power from? Well, it depends on the specific application and setup.
In the case of a solar inverter, for example, it gets its power from the solar panels. The panels generate DC power from sunlight, and the inverter then converts that power into AC power that can be used in your home. In other cases, such as with backup power systems, the inverter may get its power from a battery.
The battery stores DC power, and the inverter converts it into AC power when needed. In both cases, the inverter is an essential component that allows for the use of DC power in AC systems.
Explanation of what an inverter is and its purpose
inverters An inverter is an essential component in many electrical systems, and its purpose is to convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. DC power is typically generated by sources such as batteries or solar panels, whereas most household appliances and electronics require AC power to function. This is where inverters come in, as they enable the conversion of DC power to AC power, allowing for the safe and efficient use of electrical devices.
Think of inverters as translators for the language of electricity – they take the energy in one form and transform it into a more versatile form that can power a wide range of appliances and devices. Without inverters, we would not be able to utilize DC power in our everyday lives, as the majority of our electrical needs require AC power.

Power Sources for Inverters
In order to understand where an inverter gets its power from, it’s important to know what an inverter actually does. Essentially, an inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. This is especially useful in situations where AC power is not readily available, such as when using a solar panel or a battery.
In these cases, the inverter gets its power from the DC input and then converts it into AC power that can be used to power appliances or charge batteries. Think of it like a translator that takes one language (DC power) and translates it into another language (AC power) that can be understood by your appliances. So, whether it’s from a battery or a solar panel, an inverter gets its power from the DC source and transforms it into the AC power we need to keep our devices running.
Explanation of where inverters get their power from
“The power source for inverters varies depending on the type of inverter being used. Generally, inverters receive their power from either direct current (DC) sources or alternating current (AC) sources. DC sources can include batteries, solar panels, or wind turbines, which directly produce DC electricity.
In these cases, the inverter’s role is to convert the DC electricity into AC electricity, which is the type of electricity used in most households and commercial buildings. On the other hand, if the inverter is connected to an AC source, such as the power grid, it functions to convert the AC electricity into a form that can be used by DC devices. In either scenario, the inverter acts as a bridge between the power source and the devices requiring electricity, ensuring compatibility and efficient utilization of power.
“
Different power sources for inverters
inverters, power sources, different power sources, power inverters, renewable energy sources, battery power, solar power, wind power, grid power Power inverters are essential devices that convert DC power into AC power, allowing us to use our electronic devices and appliances when they are not close to an AC power source. These inverters come in various shapes and sizes, and they can be powered by different sources depending on your needs and availability. One common power source for inverters is batteries.
Battery-powered inverters are portable and can provide a reliable source of power when there is no access to the grid. They are especially useful for camping trips or during power outages. Another popular power source for inverters is solar power.
Solar inverters convert the DC power generated by solar panels into usable AC power. This makes them an excellent choice for off-grid systems, where you can harness the power of the sun to meet your energy needs. Additionally, wind power can also be used as a power source for inverters.
Wind inverters work by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into usable electricity. While they are not as common as solar inverters, they can be a viable option in areas with strong and consistent wind currents. Finally, grid power is another widely-used power source for inverters.
These inverters are connected to the electrical grid and can draw power from it to provide a continuous and stable source of electricity. Whether you choose to power your inverter with batteries, solar panels, wind turbines, or the grid, it’s important to consider factors such as availability, cost, and environmental impact to determine the best power source for your needs.
Direct Current (DC) Power Sources
Inverters are devices that convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. But where do they get their power from in the first place? Well, inverters typically get their power from a DC source, such as a battery or a solar panel. These DC sources provide a steady stream of power, which the inverter then converts into AC power that can be used to power household appliances or other electronic devices.
It’s kind of like having a translator who can take your message (the DC power) and convert it into a language (AC power) that can be understood by others. So, the next time you’re using an appliance that runs on AC power, remember that it all started with a DC power source and an inverter to make the conversion.
Explanation of DC power sources for inverters
Inverters are devices that convert Direct Current (DC) power into Alternating Current (AC) power, which is the type of electricity used in homes and most electrical appliances. To use an inverter, you need a reliable source of DC power. There are several options for DC power sources, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
One common DC power source is a battery, which stores electrical energy chemically and can be recharged using a charger or a renewable energy source like solar panels. Batteries are convenient because they can provide a steady supply of power even when the main grid is down. Another option is a DC power supply, which converts AC power from the grid into DC power.
This type of power source is more reliable but may not be available in all locations. Lastly, some inverters can be directly connected to a DC generator, which produces electricity through the combustion of fuel. This method provides a continuous supply of power but requires a constant fuel source.
Overall, the choice of DC power source depends on factors such as cost, availability, and the specific needs of the user.
Advantages and disadvantages of using DC power sources
Advantages and disadvantages of using DC power sources: Direct current (DC) power sources have both advantages and disadvantages. One advantage of using DC power sources is their ability to provide a steady and consistent flow of electricity. Unlike alternating current (AC) power sources, which constantly change direction, DC power sources provide a continuous stream of energy.
This makes them ideal for powering sensitive electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, which require a stable power supply. Another advantage of DC power sources is their efficiency. Since DC power flows in one direction, there is less energy lost during transmission.
This means that DC power sources can deliver more electricity to end devices, resulting in higher overall efficiency. Additionally, DC power sources can be easily converted into other forms of energy, such as mechanical energy, making them versatile and adaptable for different applications. However, there are also some disadvantages to using DC power sources.
One major disadvantage is that DC power is more difficult to transmit over long distances. AC power can be easily transformed from high voltages to lower voltages using transformers, which allows for efficient long-distance transmission. DC power, on the other hand, requires expensive and bulky equipment, such as converters and inverters, to convert the voltage and maintain the correct polarity.
Another disadvantage of DC power sources is their limited availability. AC power is readily available in homes and businesses, as it is the standard form of power supplied by utility companies. In contrast, DC power sources are less common and may require additional equipment or modifications to be used in residential or commercial settings.
In conclusion, while DC power sources have advantages such as stability and efficiency, they also have disadvantages such as limited availability and difficulty in long-distance transmission. Before deciding to use DC power sources, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of the application in order to determine if the advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Alternating Current (AC) Power Sources
When it comes to where an inverter gets its power from, the answer lies in the source of electricity it converts. An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. So, the power that an inverter receives depends on the input it is connected to.
This input can come from various sources, such as batteries, solar panels, or wind turbines. For example, if you have a solar power system, the inverter will receive its power from the solar panels, which generate DC power from sunlight. The inverter then converts this DC power into AC power that can be used to run household appliances or be fed back into the electrical grid.
Similarly, if you have a battery backup system, the inverter will draw power from the batteries and convert it into AC power. So, in essence, an inverter simply transforms the DC power it receives from a specific source into the AC power that is needed to power our devices and appliances.
Explanation of AC power sources for inverters
AC power sources for inverters
Advantages and disadvantages of using AC power sources
AC power sources, also known as Alternating Current power sources, offer several advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, AC power sources are widely available and easy to use. They are the standard power source for most household and commercial appliances, making them highly compatible with a wide range of devices.
Additionally, AC power sources can be easily converted to different voltage levels, allowing for easy distribution and transmission over long distances. Another advantage of AC power sources is that they can be generated from a variety of sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable sources such as wind and solar power. This flexibility in power generation ensures a reliable and diverse energy supply.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using AC power sources. One major drawback is that AC power can suffer from losses and inefficiencies during transmission, leading to power wastage. Another disadvantage is the potential for electrical hazards, such as electrical shocks and fires, especially if proper safety measures are not followed.
Additionally, the need for converters and transformers to convert AC power to the required voltage level can add complexity and cost to the power distribution system. In conclusion, while AC power sources offer many advantages in terms of availability and compatibility, they also come with some drawbacks that need to be addressed for efficient and safe power usage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can think of an inverter as the magician of the electric world. Just like a magician needs a source of power to perform mind-blowing tricks, an inverter also needs its own secret source of power. So, where does this sorcerer get its power from? Well, it taps into the parallel universe of direct current (DC) and transforms it into the enchanting realm of alternating current (AC).
It’s a bit like opening a portal between two worlds, with the inverter acting as the gateway. So, next time you see an inverter working its magic, remember that it’s not just pulling power out of thin air, but conjuring it up from the mystic depths of the DC universe!”
FAQs
Where does an inverter get its power from?
An inverter gets its power from a DC (direct current) source, such as a battery or solar panels, and converts it into AC (alternating current) power that can be used to run household appliances or other electrical devices.
Can an inverter be powered by a car battery?
Yes, an inverter can be powered by a car battery. In fact, many people use inverters in their vehicles to power various devices such as laptops, phones, or even small appliances while on the go.
Can an inverter be connected to a solar panel system?
Yes, an inverter can be connected to a solar panel system. In fact, this is a common setup in residential or commercial solar installations. The inverter converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be used to power the building or fed back into the grid.
What is the output power of an inverter?
The output power of an inverter is typically measured in watts or kilowatts. The specific output power will depend on the capacity or rating of the inverter. Higher capacity inverters can provide more power and can handle a greater load of electrical devices.
Can an inverter be used with a generator?
Yes, an inverter can be used with a generator. In fact, using an inverter with a generator can provide a more stable and reliable power source. The generator can produce the power, and the inverter can regulate the output to ensure a consistent supply of AC power.
How efficient are inverters in converting DC to AC power?
Inverters can vary in efficiency, but modern inverters usually have a high conversion efficiency, often above 90%. This means that they can convert a large portion of the DC power into usable AC power without significant losses.
Can an inverter be connected to a grid-tied system?
Yes, an inverter can be connected to a grid-tied system. In this setup, the inverter not only converts DC power from a source, such as solar panels or a battery, into AC power but also synchronizes the output with the utility grid. This allows excess power to be fed back into the grid and can even result in net metering or selling excess power to the utility company.
What are the different types of inverters available? A8. There are several types of inverters available, including standalone inverters, grid-tie inverters, hybrid inverters, and microinverters. Standalone inverters are used for off-grid systems, grid-tie inverters are used for grid-connected systems, hybrid inverters combine both off-grid and grid-tie capabilities, and microinverters are small inverters installed on each individual solar panel for enhanced efficiency and monitoring.
Are inverters safe to use?
Inverters are generally safe to use when properly installed and maintained. However, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines to ensure safe operation. It is also recommended to hire a qualified professional for the installation of grid-tied or complex systems to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Can an inverter be used for emergency backup power?
Yes, an inverter can be used for emergency backup power. By connecting an inverter to a battery, it can provide power during a power outage or in remote locations where there is no access to the grid. This can be particularly useful for critical equipment or appliances that need to remain operational during emergencies.