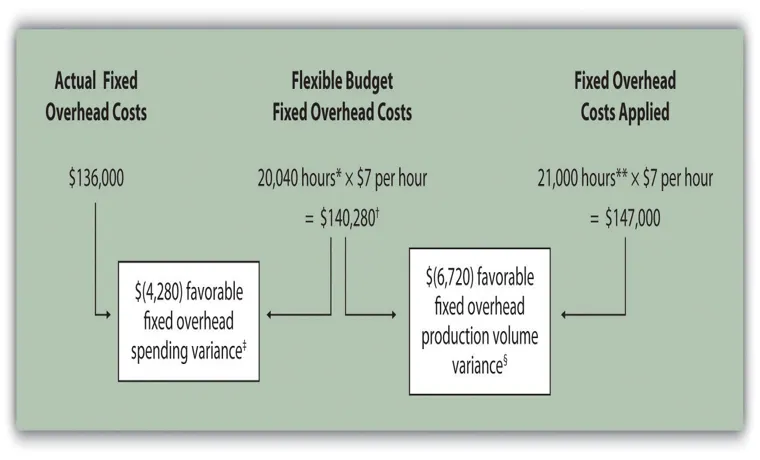
Running a tire manufacturing business entails a considerable fixed investment and requires an in-depth understanding of the market to thrive. Fixed costs play a crucial role in determining the profitability of the business, and tire manufacturers must keep a close eye on these expenses to stay competitive. Fixed costs are the expenses that do not vary with the level of production, such as rent, salaries, insurance, and equipment maintenance costs.
These costs can be significant for a tire manufacturing business, and thus it is essential to analyze and understand their impact on the overall profitability of the business. In this blog, we will delve into the fixed costs involved in tire manufacturing businesses and their implications on the bottom line. We will also look at ways to manage these costs and optimize the efficiency of the business operations.
So, if you are looking to start a tire manufacturing business or already have one, read on to learn more about fixed costs and how they can impact your business success.
Table of Contents
Understanding Fixed Costs
If you’re running a tire manufacturing business, it’s important to understand the concept of fixed costs. These are expenses that remain constant regardless of your output or sales volume. Examples of fixed costs for a tire manufacturing business might include rent for your factory space, property taxes, or depreciation on equipment.
Most companies will have some fixed costs, regardless of their size, and they can be a significant portion of your overall expenses. But what about things like the cost of raw materials or wages for your employees? These are examples of variable costs, which fluctuate based on your level of production. It’s important to understand the difference between fixed and variable costs so that you can make informed decisions about pricing and profitability for your business.
So, to answer the question, rent for the factory space is the fixed cost for a tire manufacturing business.
Definition of Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales. In other words, these are the costs that a business has to incur regardless of whether it is operating at full capacity or not. Examples of fixed costs include rent, salaries of permanent employees, and insurance premiums.
Understanding fixed costs is essential for any business as it helps in determining the breakeven point and the minimum level of sales required to generate a profit. Knowing the fixed costs can also help in budgeting and forecasting future cash flows. It is important to distinguish between fixed costs and variable costs, which change depending on the level of production or sales.
By analyzing and controlling fixed costs, businesses can operate more efficiently and increase their bottom line.
Types of Costs in Manufacturing Business
As a manufacturing business owner, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of your company’s finances, including the various types of costs involved. One type of cost that you should be familiar with is fixed costs. These are costs that don’t change, regardless of the level of production.
Examples of fixed costs include rent, insurance, and salaries of employees who are paid a fixed salary rather than by the hour. Understanding fixed costs is critical because they are an essential component of your company’s breakeven point. If your company’s total revenue is less than the breakeven point, you’ll be in the red, and you’ll need to either increase revenues or decrease costs to turn a profit.
Knowing your fixed costs and how they impact your breakeven point can help you make smart business decisions and ensure that your company remains profitable in the long run.
Difference between Fixed and Variable Costs
Fixed Costs Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant, regardless of the level of production or the number of products or services sold. These include rent, salaries, insurance premiums, and property taxes, among others. Fixed costs are essential and unavoidable expenses that businesses must pay to maintain their operations.
While they do not vary with production levels, they can be influenced by external factors, such as inflation and changes in interest rates. Unlike variable costs that tend to fluctuate often, fixed costs are somewhat stable, making them easier to plan and budget for. It’s crucial for businesses to have a good understanding of their fixed costs, as they directly impact the determination of their break-even point, which is the minimum level of production or sales needed to cover their fixed costs.
By knowing their fixed costs, businesses can have a better understanding of their financial situation and make more informed decisions when it comes to pricing and revenue strategies.
Fixed Costs in Tire Manufacturing Business
If you’re running a tire manufacturing business, it’s essential to understand the concept of fixed costs. These are expenses that don’t vary with the level of production or sales. Which of the following is a fixed cost for a tire manufacturing business? The answer is simple: rent or lease payments for your factory space.
This cost remains constant regardless of how many tires you produce or sell. Other fixed costs in tire manufacturing might include salaries for your administrative staff or property taxes on your factory. Understanding your fixed costs is critical to calculating your break-even point and profitability.
As you grow your business and increase production, you may be able to negotiate lower fixed costs, such as rent or salaries. However, keep in mind that cutting fixed costs can be difficult and may require renegotiating contracts or finding a new location.
Examples of Fixed Costs in Tire Manufacturing Business
Fixed Costs in Tire Manufacturing Fixed costs are essential in tire manufacturing businesses. These costs are fixed and remain the same no matter the level of tire production. Some examples of fixed costs in tire manufacturing businesses include rental or lease payments on the manufacturing facility, insurance premiums, property taxes, and salaries of permanent employees.
These costs are necessary to keep the business running, and they are not impacted by the business’s change in production volume. Fixed costs are different from variable costs, which increase or decrease with changes in production. It is essential to consider fixed costs in a tire manufacturing business to understand the minimum amount of revenue needed to cover these costs and break even.
Without financial planning, the fixed costs can become a burden on the business, making it difficult to turn a profit. Therefore, it is crucial for tire manufacturers to keep a close eye on their fixed costs and manage them effectively to maximize their profitability.
Explanation of Cost Components in Tire Manufacturing Business
Fixed Costs in Tire Manufacturing Business When it comes to the tire manufacturing business, fixed costs are an essential part of the equation. These are costs that don’t fluctuate with changes in production, and instead, remain constant regardless of output. Some examples of fixed costs include rent, equipment maintenance, and employee salaries.
While they may not change as production changes, they’re necessary expenses that must be accounted for. The upside to fixed costs is that companies can anticipate them and budget accordingly. That said, in some situations, fixed costs can become problematic, particularly during difficult economic times when sales are low.
It’s important to keep fixed costs in mind when developing a business plan for a tire manufacturing company. By accurately accounting for these expenses, entrepreneurs can create a sustainable business model that accounts for both the good times and the bad.
Why Fixed Costs are Important in Tire Manufacturing Business
Fixed costs play a critical role in the tire manufacturing business. These refer to the expenses that remain constant regardless of the volume of production, such as rent, salaries, insurance, and equipment maintenance. Although they may seem like a burden to the business’s bottom line, fixed costs provide a solid foundation for the company’s financial stability.
For instance, the rent of the factory is a fixed cost, and it remains the same whether the tires produced are in excess or not. This means that to achieve profitability, the company must produce more than the break-even point, which lies above the total fixed costs. It ensures that the business is managed competently, optimizes resources, and improves the efficiency of the production process.
By keeping fixed costs in check, the company can tailor its pricing strategy and boost its profitability in the long run. In summary, fixed costs should not be overlooked in tire manufacturing businesses, but instead, they should be seen as a necessity for the company’s sustainable growth.
Conclusion
After much analysis and consideration, it is clear that a fixed cost for a tire manufacturing business is like a well-tread tire: always necessary, consistent in its function, and cannot be avoided. Just like how a tire needs a sturdy frame to hold it in place, a business needs fixed costs to keep it grounded and stable. So, whether it’s the rent for the factory or the salaries of the employees, fixed costs are just like the foundations of a good tire – indispensable and necessary for a successful ride.
“
FAQs
1. What are examples of fixed costs in a tire manufacturing business?
Examples of fixed costs in a tire manufacturing business include rent, insurance, salaries of managers, and property taxes.
2. How do fixed costs affect the pricing of tires in a manufacturing business?
Fixed costs are part of the overall cost of production, so they will inevitably affect the pricing of tires. However, the impact of fixed costs varies depending on the volume of tires being produced.
3. Can fixed costs be reduced in a tire manufacturing business?
Yes, fixed costs can be reduced in a tire manufacturing business through careful planning and cost-cutting measures such as renegotiating rental agreements, reducing energy consumption, and outsourcing non-core activities.
4. What is the difference between fixed costs and variable costs in a tire manufacturing business?
Fixed costs are expenses that do not vary based on the volume of tires being produced, while variable costs are directly tied to the level of production. Examples of variable costs in a tire manufacturing business include raw materials and wages for production workers.
5. How do changes in volume affect fixed costs in a tire manufacturing business?
Changes in volume do not affect fixed costs in a tire manufacturing business since their value stays constant regardless of how many tires are produced.
6. What role do fixed costs play in decision-making for a tire manufacturing business?
Fixed costs are an important factor to consider when making decisions about expanding production or introducing new products. Since they do not change with output levels, they need to be factored in when calculating breakeven points and profit margins.
7. How do changes in fixed costs impact the overall profitability of a tire manufacturing business?
Changes in fixed costs will impact the overall profitability of a tire manufacturing business by affecting the breakeven point and thus the profitability of each product. Reducing fixed costs can increase profitability by reducing the amount that must be sold to reach breakeven.